Experts worry new strains could make vaccines less effective.Michael Ciaglo/Getty
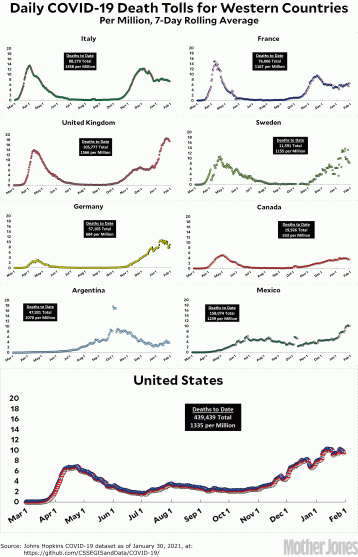
The data on COVID-19 hospitalizations and new cases looks better, for a change. After hitting a peak on January 8, the 7-day average case count is down 40 percent, according to the New York Times. Hospitalizations are improving, too, down 24 percent. This isn’t just in a few highly populated states. We’re seeing steep cliffs in new case counts all across the country—half of states have experienced at least a 50 percent drop.
Our daily update is published. States reported 2M tests, 147k cases, 97,561 people currently hospitalized with COVID-19, and 2,972 deaths. pic.twitter.com/O1eif97YOT
— The COVID Tracking Project (@COVID19Tracking) January 31, 2021
All of this is promising news. Vaccine distribution, bumbling as the rollout has been, seems to be finally doing some good.
But there are two big caveats.
Yes, for the first time since December 1 2020, hospitalizations are below the 100,000 mark, according to the COVID-19 Tracking Project. But that doesn’t mean ICU beds still aren’t nearly full (or, in the case of the hospital closest to me in the Bay Area, entirely full of 81 COVID-19 patients). There is still the possibility of a healthcare system remaining overly taxed. The peak was so high that any declines need to be taken into context of the horrific rise we saw during the first winter months.
And then there are these new strains. As COVID-19 mutates, scientists have scrambled to track new strains of the disease—potentially more infectious—that could harm the case decline researchers predicted following a projected peak in January. “We’re very worried,” Francis Collins, director of the National Institutes of Health, told the Washington Post. There are variants of the coronavirus from California, from England, and from South Africa (a strain just detected in Baltimore). Research suggests the various vaccines will work on the new strains, but the level of effectiveness for each strain, and for each vaccine, remains unclear.
For now, at least, we have some hope: The trend lines are headed in the right direction.