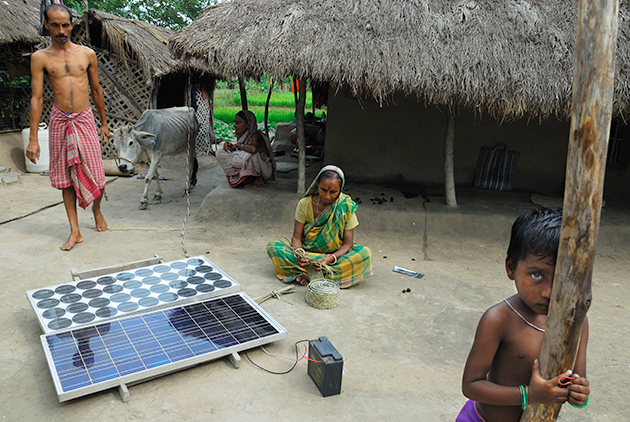
A solar panel charges in front of a house in West Bengal, India. Prasanta Biswas/ZUMA
China is by far the world’s biggest investor in clean energy technologies like solar and wind. Last year, its clean energy spending hit a record $83 billion, a 39 percent jump from the year before, and more than twice what is spent in the United States.
Although America and most other G20 nations are moving toward a clean energy overhaul, its the developing world where you’ll find the most explosive growth: When you add in emerging markets like Brazil, India, and South Africa, clean energy investment in developing countries totaled $131 billion in 2014, only six percent less than the combined total for developed countries. It’s the closest that gap has ever been, according to Bloomberg New Energy Finance (BNEF):

That gap will soon close, and then start growing in the other direction, according to a new report from the Pew Trust. Based on financial data from BNEF, the report’s authors project that more than $7 trillion will be invested in new energy systems by 2030, two-thirds of it in developing countries. (Pew’s analysis doesn’t put China in that category.) Roughly $5 trillion of it will be clean energy investment.
It’s no mystery why developing countries are positioning themselves to win this race. For one, they need the electricity. As it stands, more than 1.3 billion people, mostly in Asia, India, and sub-Saharan Africa, live without access to reliable modern service:
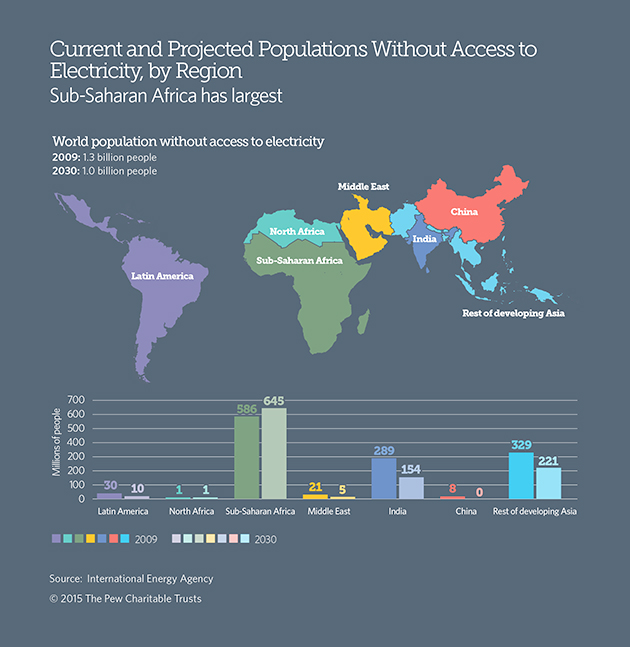
If you want to bring electricity to places without a power grid, renewables have lots of advantages. For one, it’s far cheaper and faster to build a solar or wind farm than a coal or gas-fired generation plant. And renewables can be built locally, on a small scale, eliminating the need for long-distance transmission lines. Consider what happened with cellphones: Mobile technology became cheap and ubiquitous before many African nations had landline networks, so people just “leapfrogged” straight to wireless.
The same phenomenon is afoot in the energy market, says Todd Moss, a senior fellow at the Center for Global Development, who was not involved with the Pew report. “I don’t have any doubt that over the next two generations we’ll see colossal investments in the energy sector in many African countries” and in India.
Compare the maps above and below. You’ll note a strong connection between so-called energy poverty (above) and future power demand (below), in Africa especially. This is hardly surprising, but only in the past few years has renewable energy has become affordable and accessible enough to get the transformation rolling.
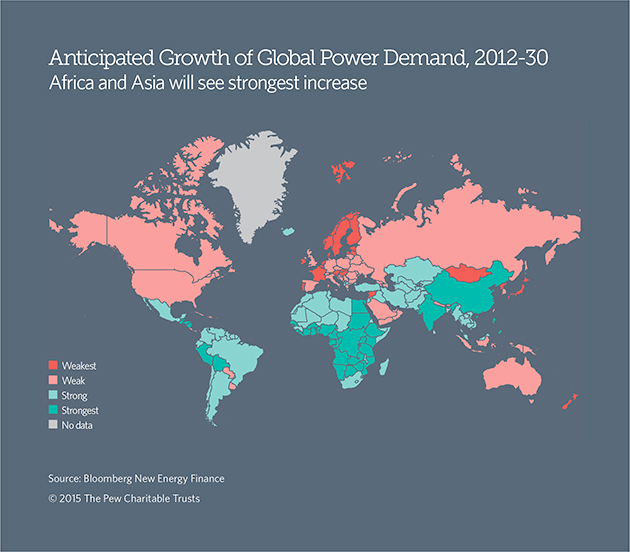
Energy poverty isn’t the only factor driving clean energy’s growth. In Bulgaria or Ukraine, both of which Pew identified as key places for energy investment in the developing world, the growth is driven by a desire to wrest control from foreign fossil fuel suppliers, i.e. Russia’s Gazprom. That’s according to Phyllis Cuttino, a clean energy analyst who authored the Pew report. “These countries want to have sources they don’t have to import, and they want to stimulate economic growth,” she said.
The report also identified Kenya, Peru, Taiwan, Morocco, Vietnam, Pakistan, and the Philippines as top attractors of clean energy investment. For now, anyway: The lineup may change from year to year in response to domestic policies (mandates, subsidies, etc.). And Moss said that the report underestimates the role African countries like Nigeria and Ethiopia will play. Still, many developing countries are in for internal political battles over clean energy, of the sort that we’ve seen, and are still fighting, in the United States.
African utility companies also often struggle with bad credit histories, Moss said, which can make it difficult to secure loans from the World Bank or other international institutions. “The key to unlocking investment in the power sector is getting a long-term, credit-worthy deal,” he said.
Regardless of which countries come out ahead, we’re almost certain to see far more money invested in clean energy than in fossil fuels over the next few decades. In the charts below, solar in particular is projected to grow massively by 2030, while new fossil fuel installations will shrink to less than half of the total.
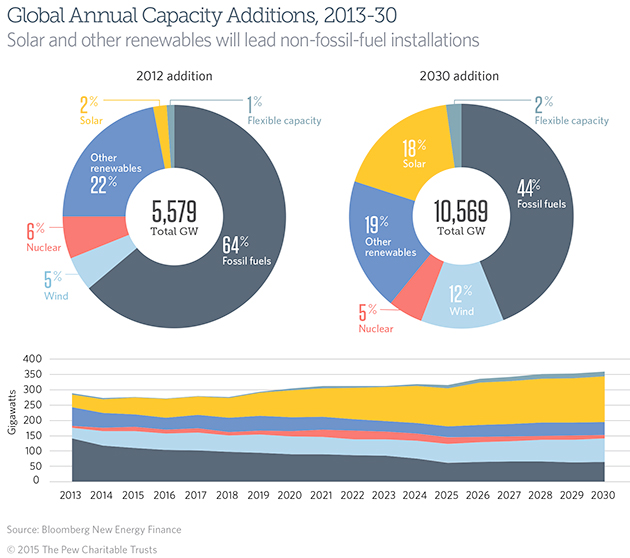
So where does this leave United States? There’s a huge opportunity for clean energy entrepreneurs to expand into developing countries, Cuttino said. Indeed, according to Commerce Department stats, six of our top 10 destinations for clean energy exports are developing countries. President Barack Obama has made electrification in Africa a signature foreign policy initiative of his second term. That move in itself sends an important signal about the difference between clean energy here and in the developing world. Here the benefits are primarily environmental. There, clean energy is seen as a key step to alleviating poverty.
















