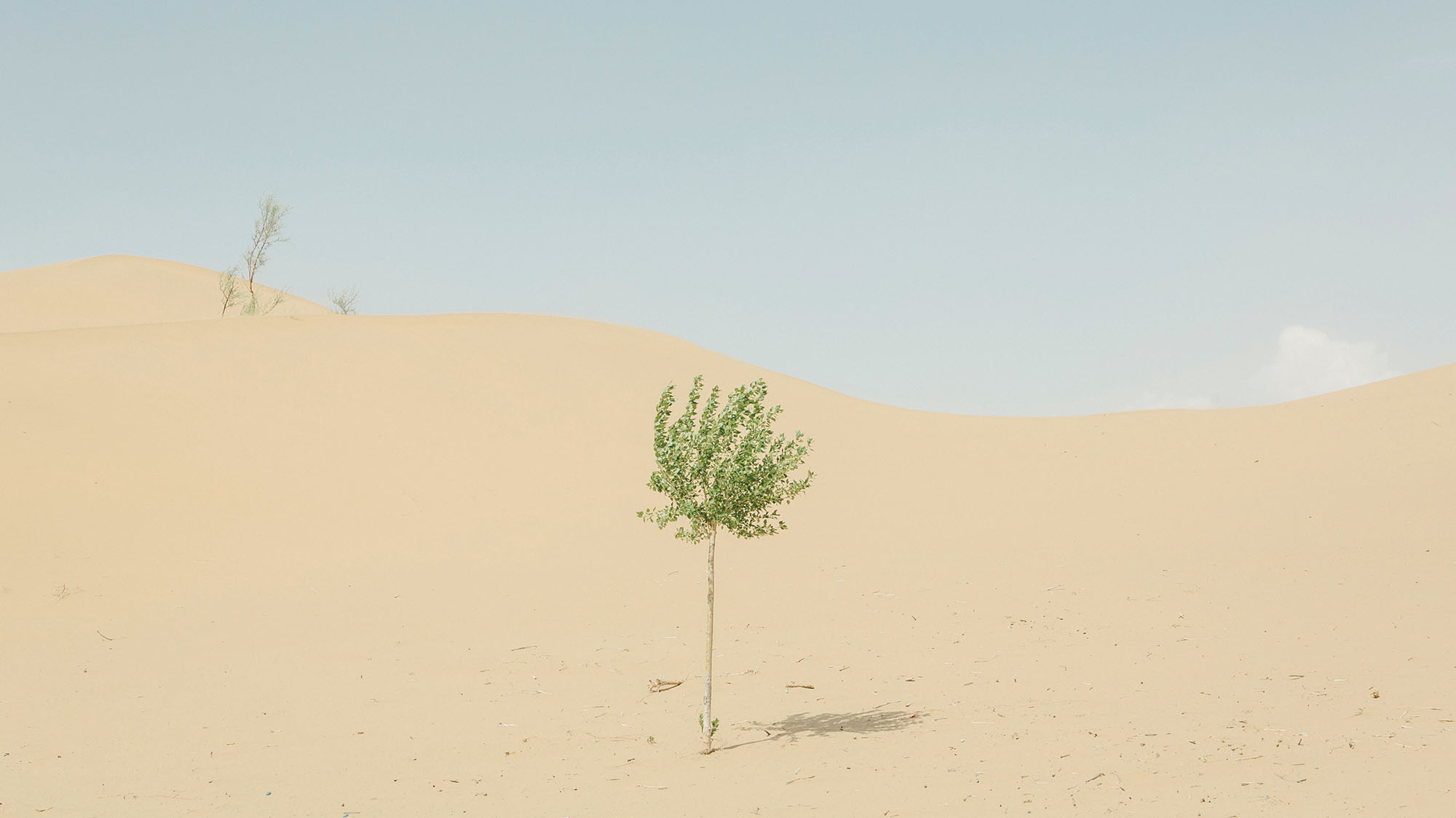
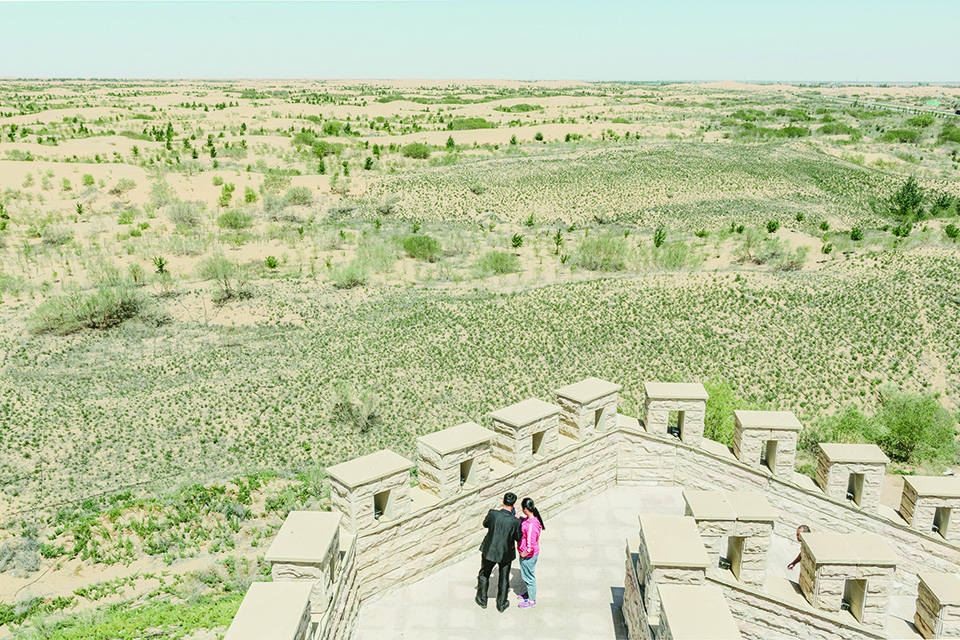
The view from the top of this windblown hill in Duolun County, in China’s Inner Mongolia region, could be described as either profoundly inspiring or deeply strange. For miles around, the earth is dun-colored and dry, stubbled with yellow grass. But the hillsides directly across from me are emblazoned with vast swaths of trees planted in geometric shapes: a square, a circle, overlapping triangles. The flatland below is striped with bands of identical young pines, standing in rigid formation like soldiers on parade.
Zuo Hongfei, the deputy director of the State Forestry Administration’s local “greening office,” directs my attention to a display with photos and satellite images showing how barren this place was just 15 years ago—a desert landscape dotted with spindly trees and shrubs. “See?” he says, pointing to one photo. “The houses were almost buried by sand!”
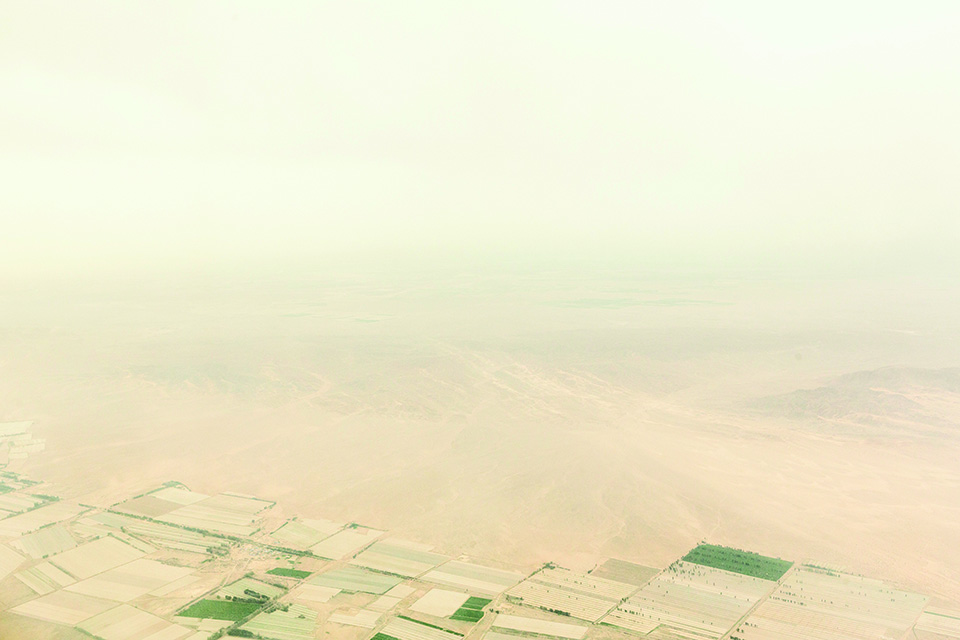

One recent estimate said China had 21,000 square miles more desert than what existed in 1975. As the Tengger expands, it is merging with two other deserts to form a vast sea of sand that could become uninhabitable.
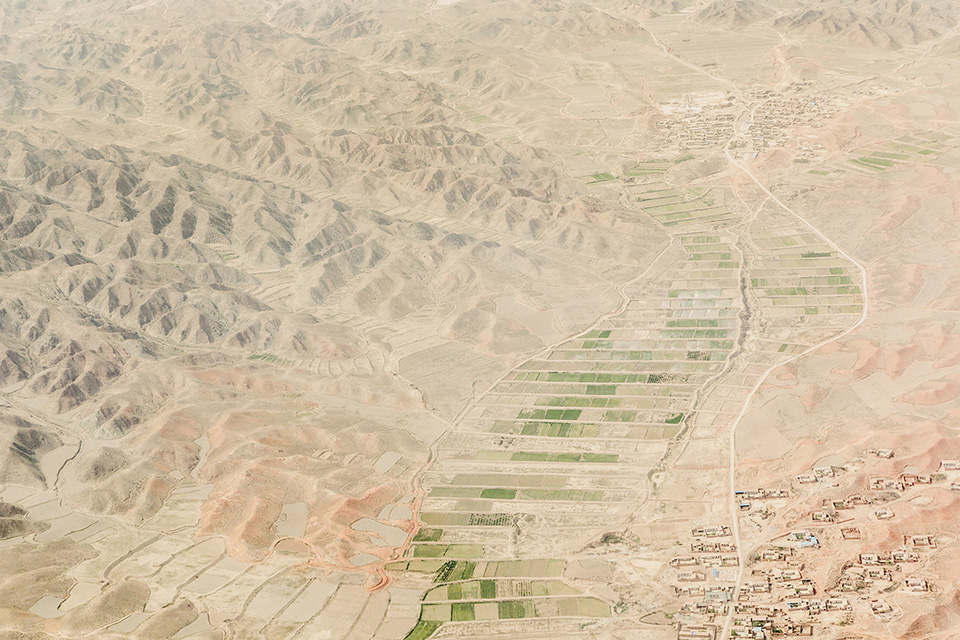
Duolun, southeast of the Gobi Desert, has always been dry. But decades of overfarming and overgrazing turned vast tracts of it into pure desert. Climate change is partly to blame, but population growth is the main culprit. The number of people in Inner Mongolia has quadrupled in the last half-century, and the number of livestock has increased sixfold. With so many people cutting trees for firewood, so many farms and factories sucking up groundwater, and so many animals chomping grass, the land simply dries up. Lacking roots to anchor it and moisture to weigh it down, fertile topsoil blows away, leaving only sand and pebbles behind.
By 2000, Duolun was up to 87 percent desert, fueling sandstorms that regularly engulfed Beijing to the south. The situation was so dire that then-Premier Zhu Rongji visited Duolun and declared, “It is imperative to build green barriers.” And build they did. Since Zhu’s pronouncement, millions of pines have been planted over a total of nearly 200,000 acres, with more going in every spring. According to official statistics, 31 percent of Duolun is now forested.
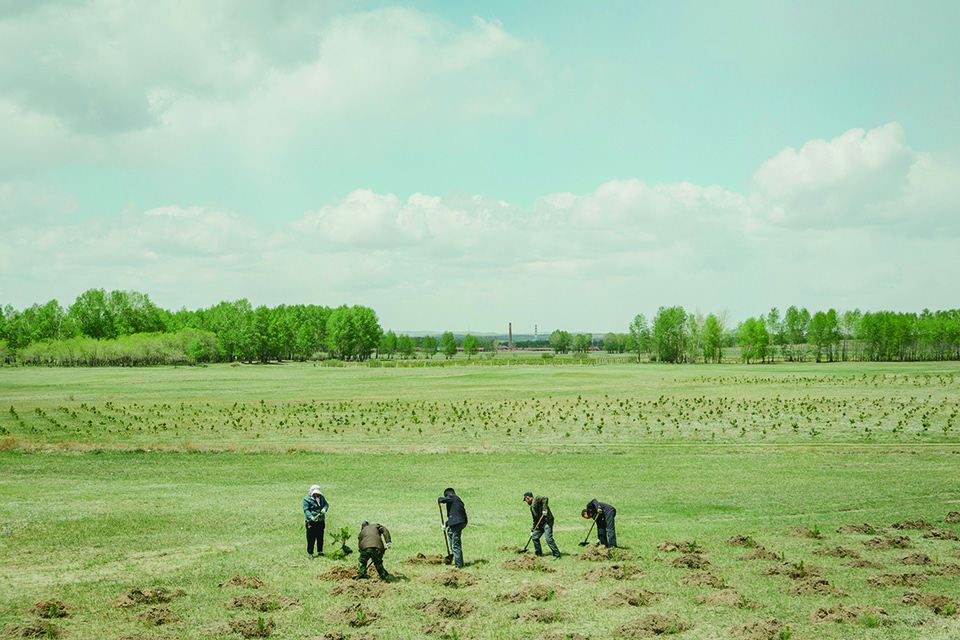

Workers planting trees.
The Duolun project is but a sliver of a titanic tree-planting effort unfolding across China. The sand lands that cover as much as 27 percent of the country have expanded rapidly—by 2006, they were devouring usable land at a rate of almost 1,000 square miles per year (nearly the area of Yosemite National Park), up from 600 square miles in the 1950s. Sand and dust regularly inundate farms and villages and shut down roads and railways. Hundreds of thousands of tons of it blow into Beijing and other cities, creating a vicious health hazard. Researchers estimate that desertification costs the Chinese economy billions of dollars per year.
China’s solution is to build a “Green Great Wall.” The Communist Party has promoted tree planting as a righteous cause, even a civic duty, for decades, but the Green Great Wall is staggeringly ambitious: By 2050, the government intends to plant 88 million acres of forests in a belt nearly 3,000 miles long and up to 900 miles wide in places. The project has global relevance. According to the United Nations, desertification directly affects more than 250 million people across the world. The United States and the Soviet Union launched massive afforestation projects in the last century, and more than two dozen African nations are today working fitfully on a green barrier against the encroaching Sahara. But China’s sylvan crusade is one of the most ambitious tests to date of whether humankind can geoengineer its way out of a major environmental problem.
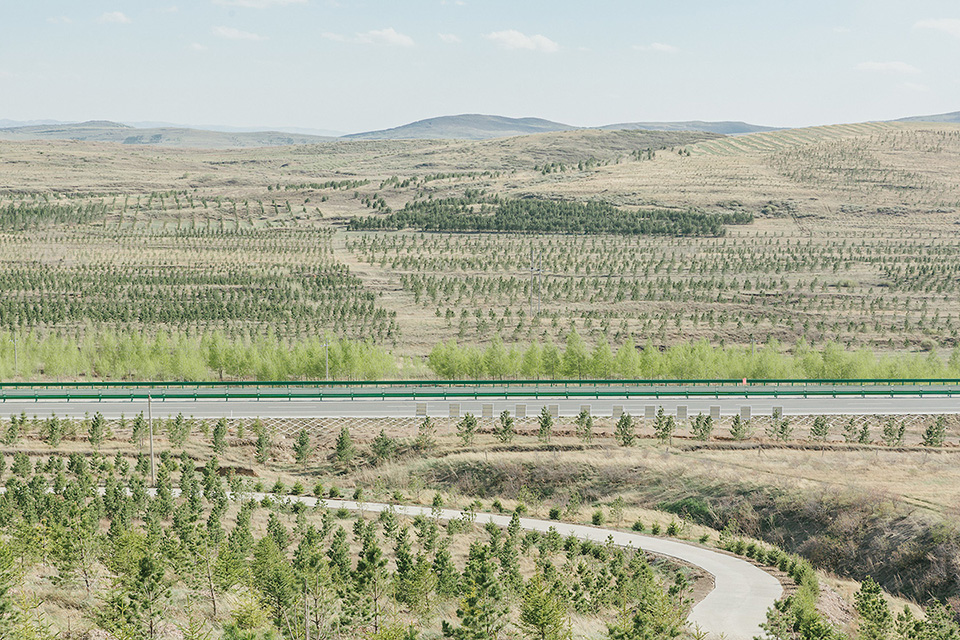

After more than a decade of the Green Great Wall, the typical landscape in Duolun today is filled with trees and shrubs. However, expert opinion is divided as to the success of the program.
The results so far have been splendid—if you believe the government. Thousands of acres of desert have been stabilized. The frequency of sandstorms nationwide fell by 20 percent between 2009 and 2014. The State Forestry Administration even claims the Green Great Wall, along with some additional planting programs it oversees, has begun to reverse the deserts’ overall expansion.
But plenty of scientists remain unimpressed. Many of the trees, planted in places they don’t grow naturally, eventually die. The survivors soak up precious groundwater that native grasses and shrubs need, causing more soil degradation. Meanwhile, thousands of farmers and herders are forced off their lands to make way for the trees. China may be winning its war against nature for now, but at what cost?
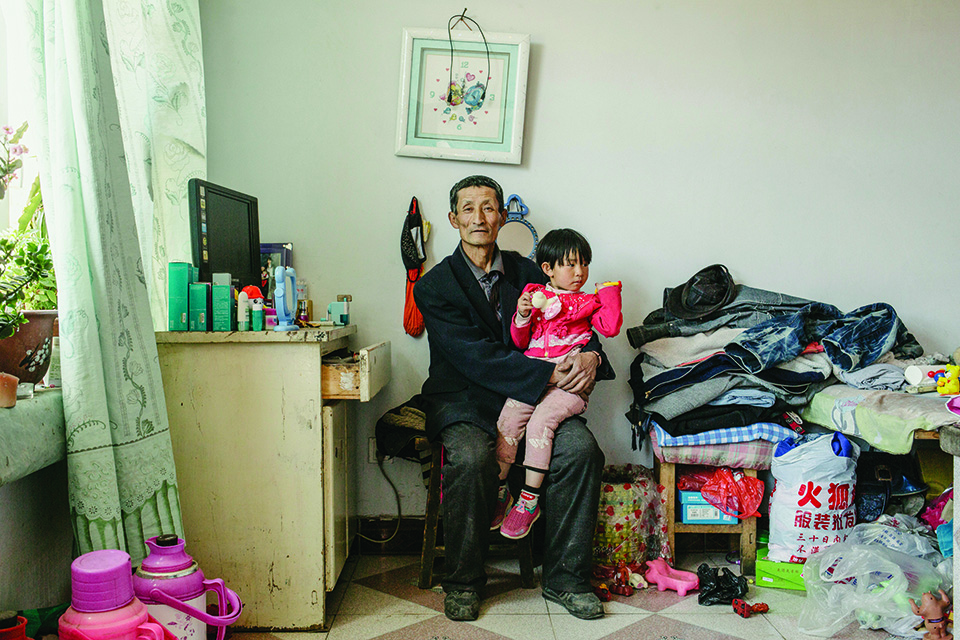

Wang Yue, 65, with his granddaugther at home. He was forced to move from his village to make way for tree planting projects.
The Green Great Wall was launched in 1978, the same year Beijing began opening up the economy, and afforestation efforts have steadily increased since then. Rather than relying on revolutionary fervor, the government now harnesses capitalism to grow trees. Villagers are paid to plant seedlings. In some places, the government leases private land for afforestation. Entrepreneurs cultivate and sell saplings and harvest mature trees for lumber. All of this has reportedly reduced poverty in many areas. It has certainly made a few people very rich.
Wang Wenbiao grew up in a family of sheep ranchers on the edge of Inner Mongolia’s vast Kubuqi Desert. “Two words were very important in my childhood,” Wang says. “Sand and poverty.”

Sand is still important to Wang, but the poverty is long gone. I meet him one spring morning in the sleek Beijing headquarters of Elion Resources Group, the multibillion-dollar company he leads. A mirthless, heavyset man of 57, he sits in a white leather chair in front of a mural depicting waterfalls and forests, flanked by company PR reps.
Wang got his break at age 28 when he was appointed to run a salt factory in the Kubuqi. “A jeep took me there, but it got stuck in the sand outside the gate,” he recalls. Sand and transport, he soon realized, were his biggest problems. As the crow flies, the salt fields were 37 miles from the railway station, but getting his cargo to the trains required a 205-mile detour via the only available road. With local government funding, Wang began building direct roads through the desert, with trees and shrubs planted alongside them to help keep the sand at bay.
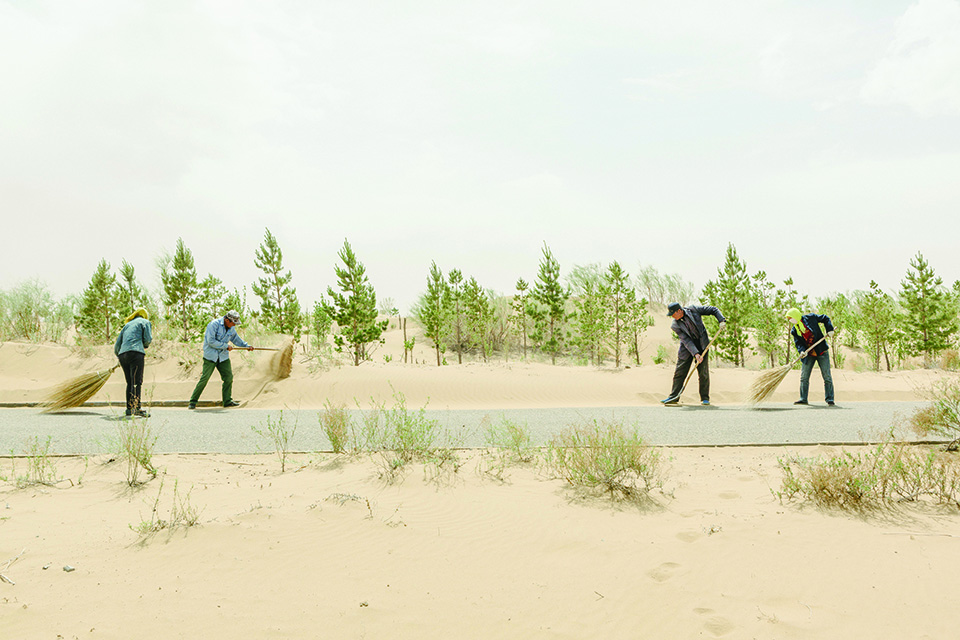

Workers clear sand off a road in the Kubuqi Desert.
Elion’s salt business boomed, and the company branched out. Today, with more than 6,000 employees and reportedly $6 billion in revenue—about half from “traditional” industries, including coal power—Elion has rebranded itself as an eco-friendly enterprise. The company runs solar power fields, cultivates desert plants prized in Chinese medicine, and claims to bring thousands of ecotourists to the Kubuqi every year. Elion is also a major Green Great Wall contractor—to date, the company has planted more than 30 percent of the Kubuqi Desert (some 2,300 square miles) and has installed instant forests in several other locations, including an area northwest of Beijing that will host the 2022 Winter Olympics. “Green land and green energy,” Wang says. “That will be the direction of our future development.”
Driving through a portion of the Kubuqi on an Elion-built road—an asphalt ribbon lined with upright rows of stubby young pines and slender poplars, most of them no taller than a fifth-grader—is a surreal experience. Beyond the trees, there is nothing but barren, rolling dunes. The road eventually leads to Elion’s palatial, dome-topped Seven Star Lakes Desert Hotel, which is surrounded by carefully irrigated rows of poplars, green lawns, and a fountain out front. The grounds include, improbably, a golf course. When a hotel staffer spots my photographer on the green, he demands the pictures be deleted. How can a desert sustain all this planting? “Everyone asks this question,” Wang told me. The trees use only a tiny amount of groundwater, he says. They are thriving, he insists, because Elion has literally made it rain. Increased transpiration from the greenery has made the climate more humid: “Twenty-nine years ago, there was only about 70 millimeters of rainfall. In recent years it has reached 400 millimeters,” Wang claims. “We changed the ecosystem.”
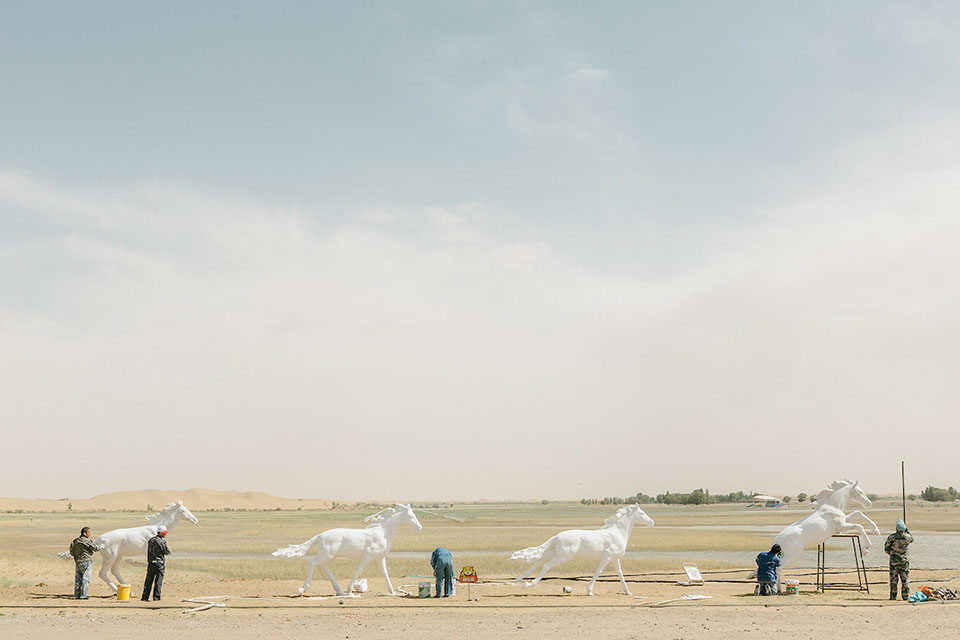


Workers paint and install horse sculptures inside Kubuqi Desert Park, north of Ordos Plateau in Inner Mongolia. The desert was one of the three major sources of sandstorms that would engulf the Beijing, Tianjin, and Hebei areas. Kubuqi is now home to around 100 species of plants and wild animals, and the park itself attracts 200,000 visitors annually.
Researchers I asked about this were skeptical. Planting an area that large might slightly increase rainfall, but to quintuple it? “I would say that’s not correct,” says Howard Diamond, a scientist at the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Cao Shixiong, a professor at Minzu University of China, offers an alternative explanation: “When it’s profitable, people tell lies.”
“The central government gives out billions of yuan every year for tree planting,” Cao, a lean, banty guy with a roguish smile, tells me when we sit down together in a university conference room. “So there are many companies that want to take part. They’re not concerned with the environment.”
Cao used to be a believer. He spent nearly 20 years working on government projects in Shaanxi province. “I thought it was a very good way to combat desertification,” he says. But many of his trees didn’t survive. “I realized it’s because of policy. We were choosing the wrong place to plant trees.”
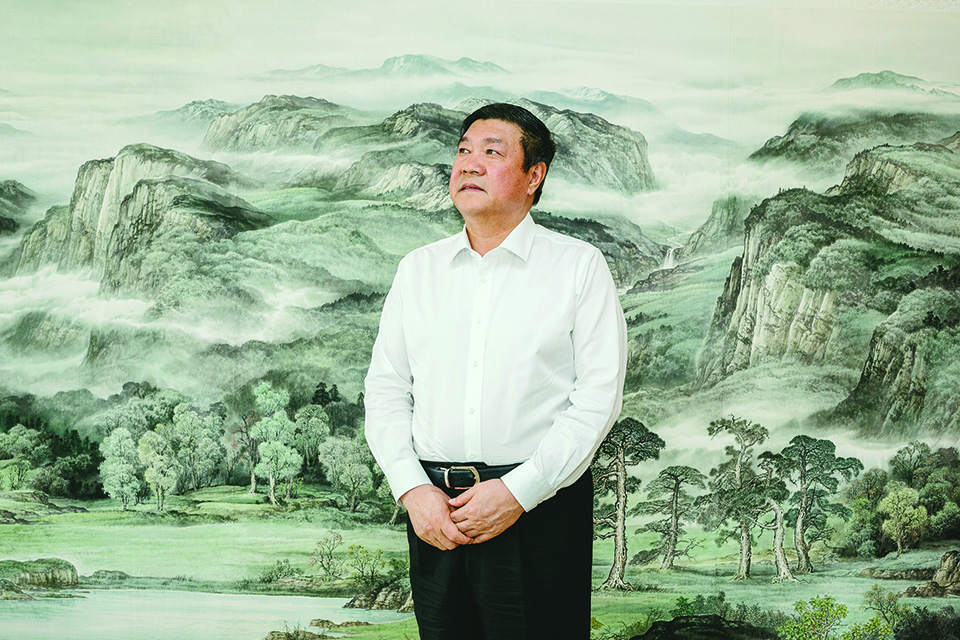

Wang Wenbiao, founder and chairman of Elion Resources Group.
He and most other critics of the greening campaign acknowledge it has helped in some places, though not to the extent the government claims. It’s undeniable that some of the billions of trees are thriving. But huge numbers have succumbed to the arid environment or diseases and pests to which monocultural forests are especially vulnerable. In 2000, a beetle infestation annihilated 1 billion poplars—two decades’ worth. Cao estimates a walloping 86 percent of the Green Great Wall trees planted since 1978 haven’t made it. (Other studies have concluded that in some regions, 60 percent of trees die over time.)
Lu Qi, head of the SFA’s Institute of Desertification Studies, smiles tolerantly when I ask about those figures. He and Cao disagree over the efficacy of the Green Great Wall. (“Anyone who works for the government is not a scientist,” Cao snorted when I told him I was meeting Lu.) Cao’s numbers are plain wrong, Lu says; contractors only get paid fully if at least 75 percent of their trees are still alive three years after planting. He points to the Duolun County project, which he helped design. “In 15 years,” Lu says, “we made trees grow in the desert.”
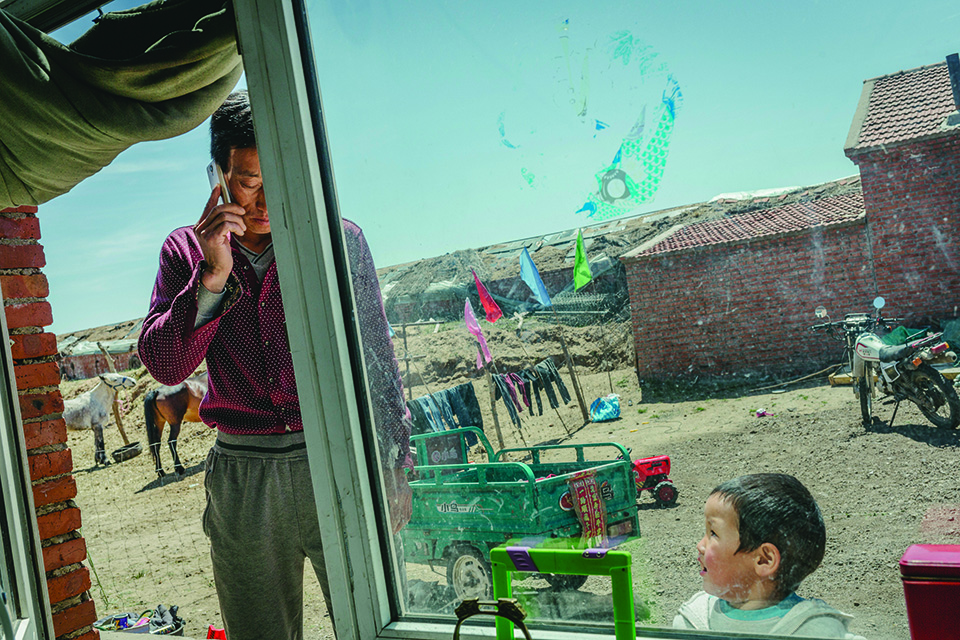

Duan Feng Quan, a horse breeder, and his son at home in New Storage Village.
The researchers’ biggest worry is that the trees are depleting subterranean aquifers so that eventually nothing will flourish. “For the past 1,000 years, only shrubs and grass have grown in those areas. Why would they think planting trees would be successful?” asks Sun Qingwei, a former Chinese Academy of Sciences desert researcher who now works for the National Geographic Society. “It’s not sustainable. Investing money in trees that are not supposed to be there is kind of crazy.”
In any case, the Green Great Wall’s long-term ecological effects may take decades to reveal themselves. Local data on the environmental and socioeconomic changes the project has already wrought is “often not available or unreliable,” explains a 2014 study by American and Chinese scientists. Another study, from the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Beijing Normal University, notes “there is surprisingly little unassailable evidence” to support claims that “the afforestation has successfully combated desertification and controlled dust storms.”
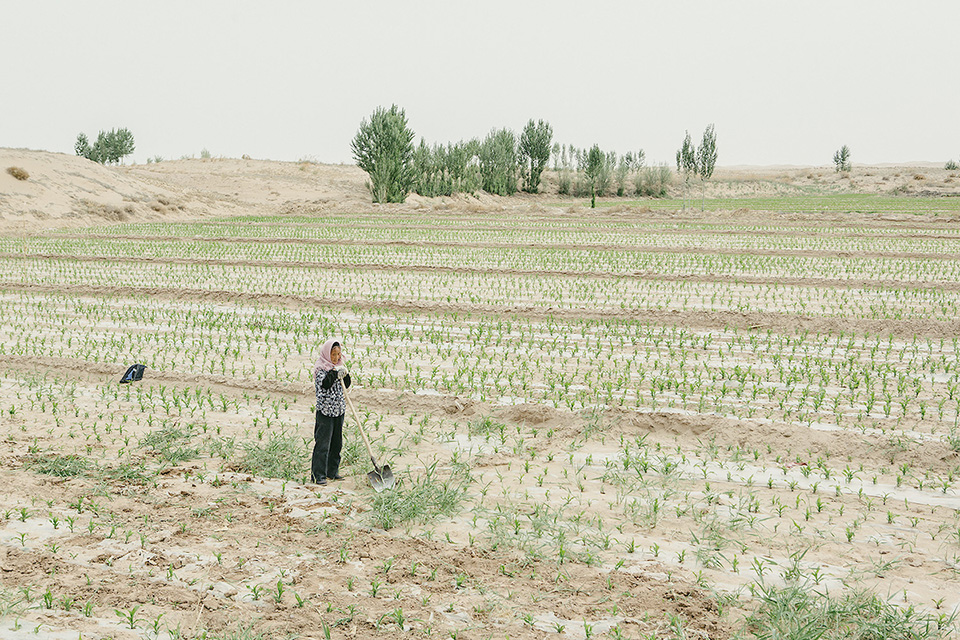

A farmer working on the edge of the desert. Trees are planted in an effort to block the wind and stabilize the soil.
State bureaucrats and researchers have ample motivation to hype the project. “Combating sand is the [government’s] project, so it has deep political meaning,” Lu acknowledges. “There are bureaucrats in every province and county,” adds Sun. “They get a lot of money for planting trees.”
The day after admiring the view from the Duolun hilltop, I drive a short distance to a grim assemblage of squat brick homes. Called New Storage Village, this settlement was built to house some of the 10,000-plus farmers forced off their land to make way for the local tree projects—across Inner Mongolia, more than 600,000 farmers and herders have met this fate. Officially, this was an effort to reduce the overgrazing that abets desertification, but many of the displaced people believe it’s just a land grab to free up resources for Han Chinese businesses; in some areas, herders have resisted with violent protests. “They would have demolished our home if we had stayed,” says Wang Yue, a sinewy 65-year-old born and raised in a now-vanished village where his family had lived for generations.
Today, Wang has a house in New Storage Village—a couple of rooms with a sleeping platform, a coal stove, and a tiny courtyard out front. “Life was better in the old village,” he says. “Here, we have to buy oats to feed the animals. We used to just let them graze.” He ekes out a living doing odd jobs, but at his age it’s getting difficult. His wife is dead and his two daughters have moved away. He never received subsidies the government promised, he says—a complaint I heard from several others here. “They lied to us,” he says. “Tree planting is making some officials rich, but we lost so many things.”
After we say our goodbyes, I walk down to where Wang’s dirt road meets the paved route through town. Off in the distance, I can make out a group of men with shovels. They are busy planting a line of spindly young trees.

Reporting for this article was supported by the Pulitzer Center on Crisis Reporting. Photos by Ian Teh/Panos.