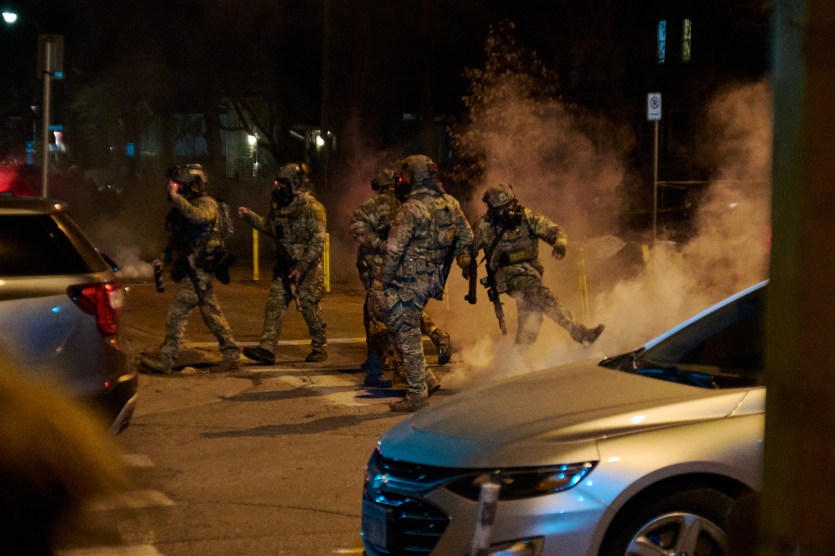Gerard Julien/AFP/Getty
This story was originally published by Wired and is shared here as part of the Climate Desk collaboration.
As the Fukushima disaster unfolded in Japan, the Blue Lake Rancheria, in Northern California, was dealing with its own crisis. Several miles inland and uphill from the Pacific Ocean, the 100 acres of tribal land had turned into a haven for roughly 3,000 coastal dwellers who were fleeing a feared tsunami from that same earthquake. A huge line of cars assembled at the Rancheria’s gas station; one young woman ran in circles, holding her baby and weeping.
Local inundation ended up being relatively minor. But the Blue Lake Rancheria was shaken. “That was an eye-opener,” says Jana Ganion, sustainability and government affairs director at the Rancheria. “We need to prepare for the disasters that are reasonably foreseeable here.”
Tsunamis for one. But also the massive earthquake that’s going to devastate the Northwest. And California’s annual wildfires, made ever more vicious by climate change. These disasters all have one thing in common: They threaten to cut the Blue Lake Rancheria off from the grid for days, maybe weeks. Tucked behind the state’s “Redwood Curtain,” the Rancheria’s rural placement affords it few access points, and roads may be inaccessible in the aftermath of a disaster.
The answer was to help pioneer what could be the future of energy in California and beyond. Working with scientists at the Schatz Energy Research Center at nearby Humboldt State University, and the local utility PG&E, the Rancheria developed its own solar-powered microgrid, allowing it to disconnect from the main grid and run off Tesla battery power. The setup powers six buildings, including a 55,000-square-foot casino and 102 hotel rooms—over 140,000 square feet of total building space.
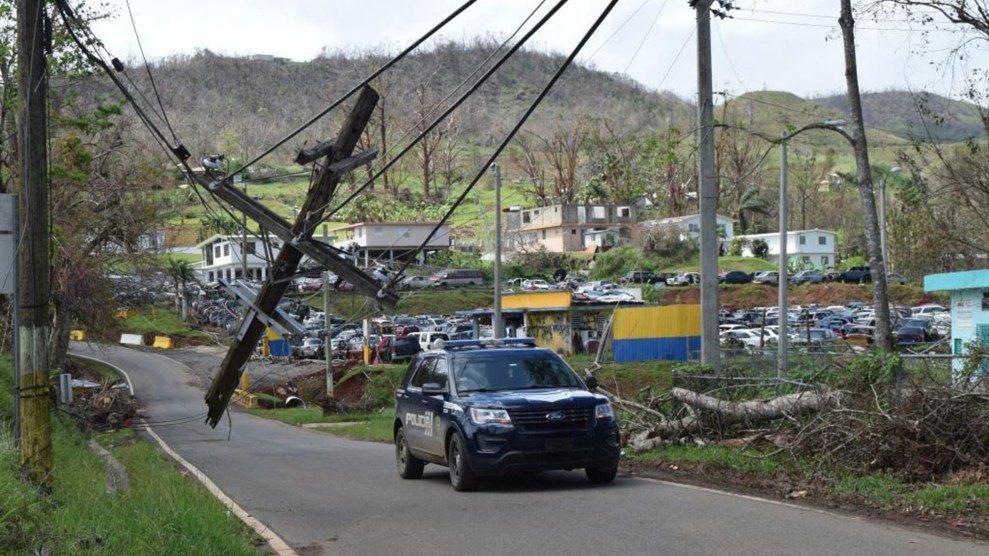
The tribe—which tallies just 49 members—is under constant threat from wildfire, along with many other communities in California. In autumn seasonal winds rustle electric equipment, showering sparks onto dry brush below. State officials have blamed PG&E for starting 17 of California’s 21 major fires in 2017 alone, as well as for last year’s devastating Camp Fire, which virtually destroyed the town of Paradise, leveling almost 20,000 buildings and killing 85. If the utility had cut power when winds near Paradise became particularly intense, that deadly blaze might never have ignited. But concerns about local hospitals and other emergency facilities tend to prevent utilities from taking such preemptive actions. Switching to microgrids during especially dangerous wind storms could keep the state’s mountain towns much safer.
But take it from the Blue Lake Rancheria: Building a microgrid isn’t so easy as throwing up a bunch of solar panels, bolting batteries to the ground, and saying au revoir to the grid at large. It takes a whole lot of time and expertise and money, about $6.3 million for the Rancheria so far—$5 million in R&D money granted by the California Energy Commission in 2015, and the rest coming from the Rancheria itself. But that research money is an investment that communities throughout California could soon benefit from.
Construction of the Rancheria’s microgrid began in May 2016, and a little over a year later, PG&E gave its blessing to begin operation. In an ideal world where the sun always shines, the Rancheria could power itself indefinitely, recharging its batteries using more than 1,500 solar panels during the day and depleting them in the evening. But on a gloomy day, such as the one on which I toured the grounds, the panels struggle to collect photons—they’re generating 120 kilowatts, compared to 420 kilowatts when the sun is cranking full-blast. On a typical day the Rancheria still draws a small amount of power from PG&E’s grid to stabilize the system. But if they lose that connection for whatever reason, those six core buildings could theoretically last for months on solar power, with backup generators kicking in at night or during periods of cloudiness.
At the entrance to the Rancheria’s offices, Dave Carter, managing research engineer at Schatz Energy Research Center, shows me a pair of flat screens. One displays a family-tree-looking diagram, with lines connecting the utility and microgrid to buildings like the hotel and casino and offices. The other screen displays a graph of energy pricing throughout the day. Noon to 6 pm is when electricity costs the most, so the system charges the batteries in the morning, so it can be discharged in the afternoon when the utility has its peak pricing.
The Rancheria is building out its system even further. It just added 167 panels above the pumps at its gas station, which it will switch on this summer. Behind the station, electricians are installing another Tesla battery pack to store that extra energy. And so long as they have the money, the tribe can add still more panels and batteries to boost its capacity and hedge against cloudy days.
Building out a microgrid, however, is no easy task for any community. “All of those buildings are going to be in various states of repair, they’re going to have various vintages of electrical systems and diesel backup generators,” says Ganion, who oversaw the project for the Rancheria. “So what we learned very quickly is that the controller on the diesel generator wasn’t smart enough to talk to the microgrid system. We had to do a bunch of work in the middle.”
Ganion hopes to turn the Rancheria’s hard-fought lessons into “a one-stop shop for communities who want to develop microgrids.” Think of it like the evolution of the personal computer: The Rancheria is basically operating as if it’s the 1980s, having to assemble a PC on its own, while one day other communities may be able to buy a microgrid that works more or less right out of the box, like a sleek modern laptop.
That might sound like something that utilities like PG&E would try to prevent. (PG&E declined to comment for this story.) Their business, after all, is in keeping customers dependent on their services. But as the world slowly moves away from fossil fuel energy plants, the utilities of the future will start to look less like energy producers and distributors, and more like just distributors. “It’s the future of the grid in California,” says Peter Lehman, founding director of the Schatz Energy Research Center.
Utilities won’t just operate power lines and other infrastructure for ferrying around electricity. Helping to develop microgrids could become part of their core business. The Rancheria’s microgrid is still in constant communication with the grid at large. “You have to work really closely with the utility on that,” says Carter, of Schatz Energy Research Center.
That interdependence means that utilities have a natural role to play in a microgrid world. The alternative is business as usual: a labyrinthine statewide network of power lines that utilities are loath to disconnect, even during high-wind events that cause and fuel wildfires, because of the liability involved in losing power to critical services.
The challenge for small, isolated communities, though, is the cost—Tesla recommends installing two of its Powerwall batteries to ensure even a small home can go a week off the grid, a system that will set you back $14,500 just in equipment costs. “What would it cost to do this, and who should be paying for it?” asks Richard Tabors, president of Tabors Caramanis Rudkevich, an energy consulting firm. “Initially, to be absolutely honest, the state of California should be paying for it.” The state is, after all, suffering an unprecedented wildfire crisis. It’s a matter of saving lives, but also of smart investing: Last November’s Camp Fire, the deadliest and most destructive in state history, caused over $16 billion in damages.
The Rancheria describes its experience with PG&E in positive terms, but others hoping to install home solar have not been so fortunate, says Bernadette Del Chiaro, executive director of the California Solar and Storage Association. “The sad thing is the utilities just have a stranglehold on policymaking and regulation making,” she says. “They absolutely are giant barriers to people being able to even just do the simple self-generation.”
Yet as California moves toward powering itself with 100 percent clean energy by 2045, making solar installations easier will become paramount. The challenge will be largely one of management, such as determining who’s responsible for maintaining different parts of the grid. Because maintenance comes with liability—you don’t want to be the one whose mismanaged equipment sparks the next deadly wildfire.
Meanwhile, the Schatz Energy Research Center is helping design a microgrid for Humboldt County’s regional airport down the road from the Blue Lake Rancheria, which will include a 9-acre solar array. And the Rancheria will keep iterating on its own microgrid, adding capacity and streamlining the overall process.
Ganion walks me through the parking lot and says the Rancheria is planning to add car shelters with solar panels. Behind the hotel and casino we find the 2-acre solar farm—panel after panel soaking up photons through the cloud cover. In its next experiment with the future of energy, she says the Rancheria might start toying with a simple form of carbon sequestration, encouraging the growth of plants underneath the panels to suck carbon dioxide out of the air.
“When you come back, we might have an herb garden growing under there,” says Ganion. “It would beat the weeds, for sure.”