Wally Skalij/Los Angeles Times/Getty/Grist
This story was originally published by Grist and is reproduced here as part of the Climate Desk collaboration.
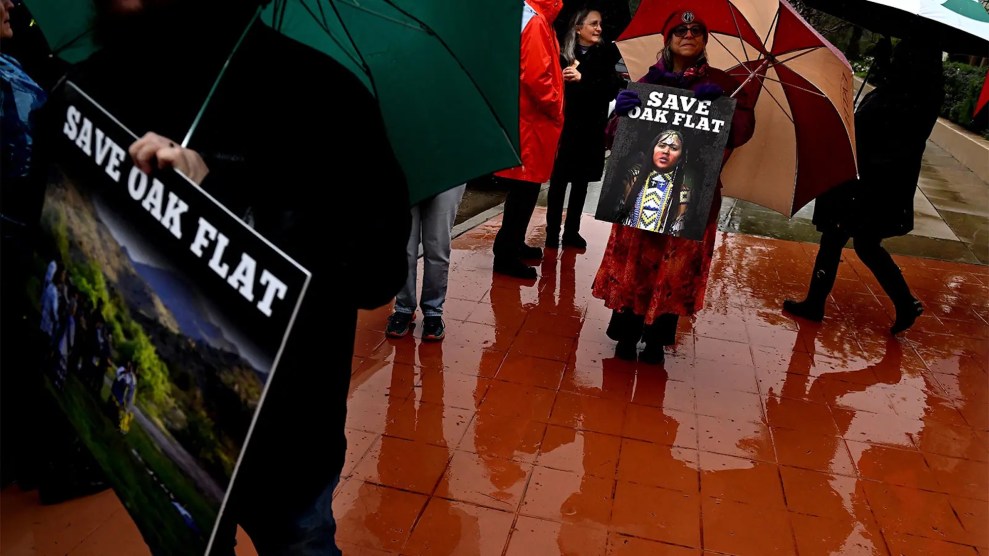
Earlier this month, the Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals declined to stop the construction of a copper mine in Arizona on land sacred to the San Carlos Apache Tribe as well as other Indigenous nations. Chí’chil Biłdagoteel, also known as Oak Flat, sits atop the third largest copper deposit on the planet and is essential to green energy projects. The operation, which will be run by Resolution Copper, a subsidiary of mining companies Rio Tinto and BHP, will leave a crater nearly 1,000 feet deep and 2 miles wide.
“Oak Flat is like Mount Sinai to us—our most sacred site where we connect with our Creator, our faith, our families and our land,” said Wendsler Noise of Apache Stronghold, a nonprofit fighting to protect the area. “We vow to appeal to the Supreme Court.”
Over the years, Oak Flat has developed a storied history. In 2014, Oak Flat was a part of a military spending bill that would allow the government to “swap” the area with other land in Arizona. In 2016, it was added to the National Register of Historic Places in an attempt to protect it, and in 2021 the Apache Stronghold sued the government, arguing that the land was reserved for the Western Apaches in an 1852 treaty. Then, in 2023, Apache Stronghold made the case that the land transfer would keep them from exercising their religion. The court disagreed.
The issue before the court illustrates a battle between religion, Indigenous rights, and potential solutions to the climate crisis. For tribal nations like the San Carlos Apache who practice what are known as “land-based religions”—ceremonial practices that are inextricably tied to areas Indigenous peoples have relationships with—preserving those lands with religious significance is paramount to the survival, and transmission, of both culture and values to the next generation.
But for developers, the proposed mine would support a few thousand jobs for the surrounding community, inject $61 billion into the local economy, and provide a critical supply of copper for everything from electric vehicles to energy storage systems. By 2031, the world will need almost 37 million metric tons of copper to continue the process of green-energy electrification. Resolution Copper said that Oak Flat could provide a quarter of US copper production.
At the heart of Apache Stronghold’s legal case is something called “substantial burden”—there must be proof that the government has interfered with an individual’s right to practice their religious beliefs. Substantial burden protects US citizens from government interference, unless the government has a really good reason. That means Apache Stronghold’s claim needs to be justified with a high level of scrutiny.
If the case goes to the Supreme Court, and Apache Stronghold wins, the federal government would need to show a compelling reason to destroy Oak Flat.
“If the Supreme Court finds that land transfer of Oak Flat is a substantial burden on Apache religious practice, then the court sends the case back down to the lower court,” said Beth Margaret Wright, who is from the Pueblo of Laguna and is an attorney with the Native American Rights Fund. “Then that would be on the government to prove that the land transfer is narrowly tailored toward a compelling government interest.”
Wright said that’s a pretty high bar for the government to meet, and it’s complicated by the court’s history with land-based religions.
According to the court’s recent decision, Oak Flat is similar to an older case out of California: Lyng v. The Northwest Indian Cemetery Protective Association. In the 1980s, the United States Forest Service was sued by the Northwest Indian Cemetery Protective Association over the proposed construction of a road. The Yurok, Karuk, and Tolowa tribes argued the road would irreparably damage an area where tribal members conducted religious ceremonies.
Ultimately, the US Supreme Court ruled that the federal government could do what it wanted with its land and said that the government couldn’t be held responsible for the religious needs of its citizens—a kind of “slippery slope” that recognized that a favorable ruling for the tribes would provide a veto button for other Indigenous nations on public projects in the future. In its ruling, the Supreme Court acknowledged that there were deeply held religious beliefs tied to the land, but the road was built anyway.
Joe Davis, an attorney with Becket Law, the firm defending Apache Stronghold, said the narrow focus on Lyng is what is at issue with Oak Flat: He says it’s the wrong framing. Five years after the Lyng decision, the Religious Freedom Restoration Act was passed. Because RFRA was written to expand religious protections, the Apache Stronghold seeks the expanded protections to be applied to Oak Flat. “This is a case, at its heart, about the Religious Freedom Restoration Act, which uses different language and is broader than the First Amendment,” said Davis.
And that argument has some history with the courts. In 2012, Becket also defended Hobby Lobby at the Supreme Court and won using the Religious Freedom Restoration Act. In that case, the court decided that under RFRA, the family that owns Hobby Lobby could opt out of providing birth control to employees under federal insurance laws due to religious beliefs. Essentially, the court found that the federal government was imposing a substantial burden because the use of birth control violated the owners’ religious freedoms.
“Hobby Lobby shows that RFRA is very powerful,” said Davis. “This case is an opportunity for the Supreme Court to make good on the promise of RFRA.”
The Ninth Circuit decided that in Oak Flat, substantial burden wasn’t met, citing the Lyng case. But the Lyng case doesn’t define substantial burden, RFRA does, and Davis argues that the court made a leap applying substantial burden when the concept wasn’t used in the Lyng case. Basically, the court didn’t use the broad protections offered by RFRA and instead applied a ruling from a pre-RFRA world.
If the case gets picked up by the US Supreme Court, and Apache Stronghold wins, this would help clarify substantial burden. But with that clarity, there may come many more legal battles testing the limits of the First Amendment for Indigenous peoples.
“It might help us in the sense that now a substantial burden is more encompassing of land-based religions,” said Beth Margaret Wright with the Native American Rights Fund. “But it doesn’t necessarily mean that our land-based religions and practices are forever protected.”
A spokesperson with the US Forest Service, the agency named in the lawsuit, declined to comment citing ongoing litigation.