<a href="http://www.shutterstock.com/cat.mhtml?lang=en&search_source=search_form&search_tracking_id=nO_Rf16oNrXX7_7yJEcyBw&version=llv1&anyorall=all&safesearch=1&searchterm=farm&search_group=&orient=&search_cat=&searchtermx=&photographer_name=&people_gender=&people_age=&people_ethnicity=&people_number=&commercial_ok=&color=&show_color_wheel=1#id=105603644&src=Wiuy-BPaD7l8v7vPpxJfyA-3-3">Maxy M</a>/Shutterstock
Earlier today the House defeated the most recent version of the Farm Bill, a $940 billion piece of legislation that regulates both food stamps and farm subsidies in the US, by a vote of 195-234.
Both Republicans and Democrats voted against the bill: Republicans complained that it didn’t create enough savings while Democrats took issue with the bill’s deep cuts to food stamps. “What is happening on the floor today was major amateur hour,” Nancy Pelosi (who was speaker when the last Farm Bill passed, in 2007) told Politico. “They didn’t get results and they put the blame on somebody else.”
The House bill would have saved an estimated $33 billion over ten years, with the majority of that savings ($21 billion) coming from cuts to food stamps, which account for almost 80 percent of farm bill spending. Part of those savings would come from requiring “asset tests” that ensure the 48 million Americans who participate in the food stamp program don’t have more than $2,000 in the bank, or own a car worth more than $5,000. Democrats including Pelosi have been saying for days that they wouldn’t vote for the bill if it included the cuts to food stamps.
The Senate’s version of the farm bill, passed last month, cut food stamps but only to the tune of $4 billion dollars. This chart from the congressional research service shows where the cuts would come from in each bill (“Nutrition” is the food stamps program):
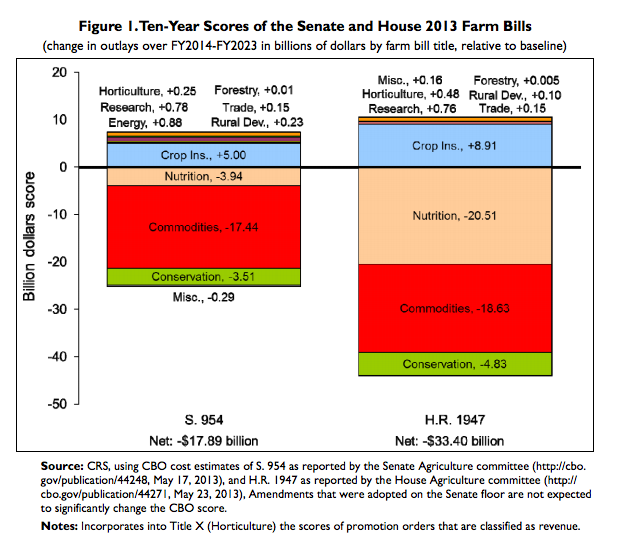
When it comes to farm subsidies, the farm bill’s other main set of policies, the bills in the House and the Senate are roughly the same. USA Today explains:
The Senate and House farm bills are largely similar when it comes to farm policy issues, with both measures streamlining conservation programs, expanding the federally subsidized crop insurance program and slashing subsidy payments—including the elimination of the $5 billion a year in direct payments doled out to farmers regardless of whether they grow crops. In a bid to help Southern growers who depend on direct payments, each bill would set higher support prices for rice and peanut farmers, meaning growers would see subsidy payments kick in sooner.
But a significant divide exists between the two chambers in the scope of proposed cuts to the country’s food stamp program, now known as the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program, that will likely continue to be a sticking point in determining whether the farm bill passes.
Congress now has until January 1st to pass a new Farm Bill, though it’s unclear when the House will bring the bill back up for a vote again. “If it doesn’t pass, I don’t know if it’s going to come up again in this Congress,” Congressman Frank Lucas (R-Okl.), chair of the House agriculture committee who had steered the bill to a vote today, told the New York Times before today’s vote.