Photo: Larry Sultan
Update (4/25/14): An FDA advisory panel has recommended banning the kind of devices used on students at the Rottenberg school.
Update (9/4/12): Jennifer Gonnerman wrote this update in New York magazine to her epic 2007 Mother Jones exposé on torture at the “school of shock.”
Rob Santana awoke terrified. He’d had that dream again, the one where silver wires ran under his shirt and into his pants, connecting to electrodes attached to his limbs and torso. Adults armed with surveillance cameras and remote-control activators watched his every move. One press of a button, and there was no telling where the shock would hit—his arm or leg or, worse, his stomach. All Rob knew was that the pain would be intense.
Every time he woke from this dream, it took him a few moments to remember that he was in his own bed, that there weren’t electrodes locked to his skin, that he wasn’t about to be shocked. It was no mystery where this recurring nightmare came from—not A Clockwork Orange or 1984, but the years he spent confined in America’s most controversial “behavior modification” facility.
In 1999, when Rob was 13, his parents sent him to the Judge Rotenberg Educational Center, located in Canton, Massachusetts, 20 miles outside Boston. The facility, which calls itself a “special needs school,” takes in all kinds of troubled kids—severely autistic, mentally retarded, schizophrenic, bipolar, emotionally disturbed—and attempts to change their behavior with a complex system of rewards and punishments, including painful electric shocks to the torso and limbs. Of the 234 current residents, about half are wired to receive shocks, including some as young as nine or ten. Nearly 60 percent come from New York, a quarter from Massachusetts, the rest from six other states and Washington, D.C. The Rotenberg Center, which has 900 employees and annual revenues exceeding $56 million, charges $220,000 a year for each student. States and school districts pick up the tab.
The Rotenberg Center is the only facility in the country that disciplines students by shocking them, a form of punishment not inflicted on serial killers or child molesters or any of the 2.2 million inmates now incarcerated in U.S. jails and prisons. Over its 36-year history, six children have died in its care, prompting numerous lawsuits and government investigations. Last year, New York state investigators filed a blistering report that made the place sound like a high school version of Abu Ghraib. Yet the program continues to thrive—in large part because no one except desperate parents, and a few state legislators, seems to care about what happens to the hundreds of kids who pass through its gates.
In Rob Santana’s case, he freely admits he was an out-of-control kid with “serious behavioral problems.” At birth he was abandoned at the hospital, traces of cocaine, heroin, and alcohol in his body. A middle-class couple adopted him out of foster care when he was 11 months old, but his troubles continued. He started fires; he got kicked out of preschool for opening the back door of a moving school bus; when he was six, he cut himself with a razor. His mother took him to specialists, who diagnosed him with a slew of psychiatric problems: attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, post-traumatic stress disorder, bipolar disorder, and obsessive-compulsive disorder.
Rob was at the Rotenberg Center for about three and a half years. From the start, he cursed, hollered, fought with employees. Eventually the staff obtained permission from his mother and a Massachusetts probate court to use electric shock. Rob was forced to wear a backpack containing five two-pound, battery-operated devices, each connected to an electrode attached to his skin. “I felt humiliated,” he says. “You have a bunch of wires coming out of your shirt and pants.” Rob remained hooked up to the apparatus 24 hours a day. He wore it while jogging on the treadmill and playing basketball, though it wasn’t easy to sink a jump shot with a 10-pound backpack on. When he showered, a staff member would remove his electrodes, all except the one on his arm, which he had to hold outside the shower to keep it dry. At night, Rob slept with the backpack next to him, under the gaze of a surveillance camera.
Employees shocked him for aggressive behavior, he says, but also for minor misdeeds, like yelling or cursing. Each shock lasts two seconds. “It hurts like hell,” Rob says. (The school’s staff claim it is no more painful than a bee sting; when I tried the shock, it felt like a horde of wasps attacking me all at once. Two seconds never felt so long.) On several occasions, Rob was tied facedown to a four-point restraint board and shocked over and over again by a person he couldn’t see. The constant threat of being zapped did persuade him to act less aggressively, but at a high cost. “I thought of killing myself a few times,” he says.
Rob’s mother Jo-Anne deLeon had sent him to the Rotenberg Center at the suggestion of the special-ed committee at his school district in upstate New York, which, she says, told her that the program had everything Rob needed. She believed he would receive regular psychiatric counseling—though the school does not provide this.
As the months passed, Rob’s mother became increasingly unhappy. “My whole dispute with them was, ‘When is he going to get psychiatric treatment?'” she says. “I think they had to get to the root of his problems—like why was he so angry? Why was he so destructive? I really think they needed to go in his head somehow and figure this out.” She didn’t think the shocks were helping, and in 2002 she sent a furious fax demanding that Rob’s electrodes be removed before she came up for Parents’ Day. She says she got a call the next day from the executive director, Matthew Israel, who told her, “You don’t want to stick with our treatment plan? Pick him up.” (Israel says he doesn’t remember this conversation, but adds, “If a parent doesn’t want the use of the skin shock and wants psychiatric treatment, this isn’t the right program for them.”)
Rob’s mother is not the only parent angry at the Rotenberg Center. Last year, Evelyn Nicholson sued the facility after her 17-year-old son Antwone was shocked 79 times in 18 months. Nicholson says she decided to take action after Antwone called home and told her, “Mommy, you don’t love me anymore because you let them hurt me so bad.” Rob and Antwone don’t know each other (Rob left the facility before Antwone arrived), but in some ways their stories are similar. Antwone’s birth mother was a drug addict; he was burned on an electric hot plate as an infant. Evelyn took him in as a foster child and later adopted him. The lawsuit she filed against the Rotenberg Center set off a chain of events: investigations by multiple government agencies, emotional public hearings, scrutiny by the media. Legislation to restrict or ban the use of electric shocks in such facilities has been introduced in two state legislatures. Yet not much has changed.
Rob has paid little attention to the public debate over his alma mater, though he visits its website occasionally to see which of the kids he knew are still there. After he left the center he moved back in with his parents. At first glance, he seems like any other 21-year-old: baggy Rocawear jeans, black T-shirt, powder-blue Nikes. But when asked to recount his years at the Rotenberg Center, he speaks for nearly two hours in astonishing detail, recalling names and specific events from seven or eight years earlier. When he describes his recurring nightmares, he raises both arms and rubs his forehead with his palms.
Despite spending more than three years at this behavior-modification facility, Rob still has problems controlling his behavior. In 2005, he was arrested for attempted assault and sent to jail. (This year he was arrested again, for drugs and assault.) Being locked up has given him plenty of time to reflect on his childhood, and he has gained a new perspective on the Rotenberg Center. “It’s worse than jail,” he told me. “That place is the worst place on earth.”
One Punishment Fits All
The story of the Rotenberg Center is in many ways a tale of two schools. Slightly more than half the residents are what the school calls “high functioning”: kids like Rob and Antwone, who have diagnoses like attention-deficit disorder, bipolar disorder, post-traumatic stress disorder, and other emotional problems. The other group is even more troubled. Referred to as “low functioning,” it includes kids with severe autism and mental retardation; most cannot speak or have very limited verbal abilities. Some have behaviors so extreme they can be life threatening: chomping on their hands and arms, running into walls, nearly blinding themselves by banging their heads on the floor again and again.
The Rotenberg Center has long been known as the school of last resort—a place that will take any kid, no matter how extreme his or her problems are. It doesn’t matter if a child has been booted out of 2, 5, 10, or 20 other programs—he or she is still welcome here. For desperate parents, the Rotenberg Center can seem like a godsend. Just ask Louisa Goldberg, the mother of 25-year-old Andrew, who has severe mental retardation. Andrew’s last residential school kicked him out after he kept assaulting staff members; the Rotenberg Center was the only place willing to accept him. According to Louisa, Andrew’s quality of life has improved dramatically since 2000, when he was hooked up to the shock device, known as the Graduated Electronic Decelerator, or ged.
The Rotenberg Center has a policy of not giving psychiatric drugs to students—no Depakote, Paxil, Risperdal, Ritalin, or Seroquel. It’s a policy that appeals to Louisa and many other parents. At Andrew’s last school, she says, “he had so many medicines in him he’d take a two-hour nap in the morning, he’d take a two-hour nap in the afternoon. They’d have him in bed at eight o’clock at night. He was sleeping his life away.” These days, Louisa says she is no longer afraid when her son comes home to visit. “[For him] to have an electrode on and to receive a ged is to me a much more favorable way of dealing with this,” she says. “He’s not sending people to the hospital.”
Marguerite Famolare brought her son Michael to the Rotenberg Center six years ago, after he attacked her so aggressively she had to call 911 and, in a separate incident, flipped over a kitchen table onto a tutor. Michael, now 19, suffers from mental retardation and severe autism. These days, when he comes home for a visit, Marguerite carries his shock activator in her purse. All she has to do, she says, is show it to him. “He’ll automatically comply to whatever my signal command may be, whether it is ‘Put on your seatbelt,’ or ‘Hand me that apple,’ or ‘Sit appropriately and eat your food,'” she says. “It’s made him a human being, a civilized human being.”
Massachusetts officials have twice tried to shut the Rotenberg Center down—once in the 1980s and again in the 1990s. Both times parents rallied to its defense, and both times it prevailed in court. (See “Why Can’t Massachusetts Shut Matthew Israel Down?” page 44.) The name of the center ensures nobody forgets these victories; it was Judge Ernest Rotenberg, now deceased, who in the mid-’80s ruled that the facility could continue using aversives—painful punishments designed to change behavior—so long as it obtained authorization from the Bristol County Probate and Family Court in each student’s case. But even though the facility wasn’t using electric shock when this ruling was handed down, the court rarely, if ever, bars the Rotenberg Center from adding shock to a student’s treatment plan, according to lawyers and disability advocates who have tried to prevent it from doing so.
Since Evelyn Nicholson filed her lawsuit in 2006, the Rotenberg Center has faced a new wave of criticism and controversy. (See “Nagging? Zap. Swearing? Zap,” page 41.) And again, the facility has relied heavily on the testimonials of parents like Louisa Goldberg and Marguerite Famolare to defend itself. Not surprisingly, the most vocal parent-supporters tend to be those with the sickest children, since they are the ones with the fewest options. But at the Rotenberg Center, the same methods of “behavior modification” are applied to all kids, no matter what is causing their behavior problems. And so, while Rob would seem to have little in common with mentally retarded students like Michael and Andrew, they all shared a similar fate once their parents placed them under the care of the same psychologist, a radical behaviorist known as Dr. Israel.
Dr. Israel’s Radical Behavior
In 1950, matt israel was a Harvard freshman looking to fill his science requirement. He knew little about B.F. Skinner when he signed up for his course, Human Behavior. Soon, though, Israel became fascinated with Skinner’s scientific approach to the study of behavior, and he picked up Walden Two, Skinner’s controversial novel about an experimental community based on the principles of behaviorism. The book changed Israel’s life. “I decided my mission was to start a utopian community,” he says. Israel got a Ph.D. in psychology in 1960 from Harvard, and started two communal houses outside Boston.
One of the people Israel lived with was a three-year-old named Andrea, the daughter of a roommate. The two did not get along. “She was wild and screaming,” Israel recalls. “I would retreat to my own room, and she’d be trying to pull away and get into my room, and I’d have to hold the door on one side to keep her from disturbing me.” When company would come over, he says, “She would walk around with a toy broom and whack people over the head.”
Through experiments with rats and pigeons, Skinner had demonstrated how animals learn from the consequences of their actions. With permission from Andrea’s mother, Israel decided to try out Skinner’s ideas on the three-year-old. When Andrea was well behaved, Israel took her out for walks. But when she misbehaved, he punished her by snapping his finger against her cheek. His mentor Skinner preached that positive reinforcement was vastly preferable to punishment, but Israel says his methods transformed the girl. “Instead of being an annoyance, she became a charming addition to the house.”
Israel’s success with Andrea convinced him to start a school. In 1971, he founded the Behavior Research Institute in Rhode Island, a facility that would later move to Massachusetts and become known as the Judge Rotenberg Center. Israel took in children nobody else wanted—severely autistic and mentally retarded kids who did dangerous things to themselves and others. To change their behavior, he developed a large repertoire of punishments: spraying kids in the face with water, shoving ammonia under their noses, pinching the soles of their feet, smacking them with a spatula, forcing them to wear a “white-noise helmet” that assaulted them with static.
In 1977, Israel opened a branch of his program in California’s San Fernando Valley, along with Judy Weber, whose son Tobin is severely autistic. Two years later, the Los Angeles Times reported Israel had pinched the feet of Christopher Hirsch, an autistic 12-year-old, at least 24 times in 30 minutes, while the boy screamed and cried. This was a punishment for soiling his pants. (“It might have been true,” Israel says. “It’s true that pinches were being used as an aversive. The pinch, the spank, the muscle squeeze, water sprays, bad taste—all those procedures were being used.”) Israel was in the news again in 1981, when another student, 14-year-old Danny Aswad, died while strapped facedown to his bed. In 1982, the California Department of Social Services compiled a 64-page complaint that read like a catalog of horrors, describing students with bruises, welts, and cuts. It also accused Israel of telling a staff member “to grow his fingernails longer so he could give an effective pinch.”
In 1982, the facility settled with state officials and agreed to stop using physical punishments. Now called Tobinworld, and still run by Judy Weber, it is a $10-million-a-year organization operating day schools near Los Angeles and San Francisco. The Rotenberg Center considers itself a “sister school” to Tobinworld, and Israel makes frequent trips to California to visit Weber. The two were married last year.
Despite his setback in California, Israel continued to expand on the East Coast—and to generate controversy. In 1985, Vincent Milletich, an autistic 22-year-old, suffered a seizure and died after he was put in restraints and forced to wear a white-noise helmet. Five years later, 19-year-old Linda Cornelison, who had the mental capacity of a toddler, refused to eat. On the bus to school, she clutched her stomach; someone had to carry her inside, and she spent the day on a couch in a classroom. Linda could not speak, and the staff treated her actions as misbehaviors. Between 3:52 p.m. and 8 p.m., staffers punished her with 13 spatula spankings, 29 finger pinches, 14 muscle squeezes, and 5 forced inhalings of ammonia. It turned out that Linda had a perforated stomach. She died on the operating table at 1:45 a.m.
The local district attorney’s office examined the circumstances of Vincent’s death but declined to file any charges. In Linda’s case, the Massachusetts Department of Mental Retardation investigated and found that while Linda’s treatment had “violated the most basic codes and standards of decency and humane treatment,” there was insufficient evidence to prove that the use of aversives had caused her death.
By the time Linda died, Israel was moving away from spatulas and toward electric shock, which, from his perspective, offered many advantages. “To give a spank or a muscle squeeze or a pinch, you had to control the student physically, and that could lead to a struggle,” he says. “A lot of injuries were occurring.” Since shocking only required pressing a button, Israel could eliminate the need for employees to wrestle a kid to the ground. Another benefit, he says, was increased consistency. It was hard to know if one staff member’s spatula spanking was harder than another’s, but it was easy to measure how many times a staff member had shocked a child.
Israel purchased a shock device then on the market known as sibis—Self-Injurious Behavior Inhibiting System—that had been invented by the parents of an autistic girl and delivered a mild shock that lasted .2 second. Between 1988 and 1990, Israel used sibis on 29 students, including one of his most challenging, Brandon, then 12, who would bite off chunks of his tongue, regurgitate entire meals, and pound himself on the head. At times Brandon was required to keep his hands on a paddle; if he removed them, he would get automatic shocks, one per second. One infamous day, Brandon received more than 5,000 shocks. “You have to realize,” Israel says. “I thought his life was in the balance. I couldn’t find any medical solution. He was vomiting, losing weight. He was down to 52 pounds. I knew it was risky to use the shock in large numbers, but if I persevered that day, I thought maybe it would eventually work. There was nothing else I could think of to do…but by the time it went into the 3,000 or 4,000 range, it became clear it wasn’t working.”
This day was a turning point in the history of Israel’s operation—that’s when he decided to ratchet up the pain. The problem, he decided, was that the shock sibis emitted was not strong enough. He says he asked sibis‘s manufacturer, Human Technologies, to create a more powerful device, but it refused. “So we had to redesign the device ourselves,” he says. He envisioned a device that would start with a low current but that could increase the voltage if needed—hence its name, Graduated Electronic Decelerator or ged—but he abandoned this idea early on. “As it turns out, that’s really not a wise approach,” he says. “It’s sort of like operating a car and wearing out the brakes because you never really apply them strongly enough. Instead, we set it at a certain level that was more or less going to be effective for most of our students.”
Thirty years earlier, O. Ivar Lovaas, a psychology professor at ucla, had pioneered the use of slaps and screams and electric jolts to try to normalize the behavior of autistic kids. Life magazine featured his work in a nine-page photo essay in 1965 with the headline, “A surprising, shocking treatment helps far-gone mental cripples.” Lovaas eventually abandoned these methods, telling cbs in 1993 that shock was “only a temporary suppression” because patients become inured to the pain. “These people are so used to pain that they can adapt to almost any kind of aversive you give them,” he said.
Israel encountered this same sort of adaptation in his students, but his solution was markedly different: He decided to increase the pain once again. Today, there are two shock devices in use at the Rotenberg Center: the ged and the ged-4. The devices look similar and both administer a two-second shock, but the ged-4 is nearly three times more powerful—and the pain it inflicts is that much more severe.
The Mickey Mouse Club
Ten years ago, Israel hung up a Mickey Mouse poster in the main hall, and he noticed that it made people smile—so he bought every Mickey Mouse poster he could find. He hung them in the corridors and even papered the walls of what became known as the Mickey Mouse Conference Room. Entering the Rotenberg Center is a bit like stepping into a carnival fun house, I discovered during a two-day visit last autumn. Two brushed-aluminum dogs, each nearly 5 feet tall and sporting a purple neon collar, stand guard outside. Giant silver stars dangle from the lobby ceiling; the walls and chairs in the front offices are turquoise, lime green, and lavender.
Israel, 74, still holds the title of executive director, for which he pays himself nearly $400,000 in salary and benefits. He appears utterly unimposing: short and slender with soft hands, rounded shoulders, curly white hair, paisley tie. Then he sits down beside me and, unprompted, starts talking about shocking children. “The treatment is so powerful it’s hard not to use if you have seen how effective it is,” he says quietly. “It’s brief. It’s painful. But there are no side effects. It’s two seconds of discomfort.” His tone is neither defensive nor apologetic; rather, it’s perfectly calm, almost soothing. It’s the sort of demeanor a mother might find comforting if she were about to hand over her child.
Before we set off on our tour of the facility, there’s something Israel wants me to see: Before & After, a homemade movie featuring six of his most severe cases. Israel has been using some of the same grainy footage for more than two decades, showing it to parents of prospective students as well as visiting reporters. They’ve already mailed me a copy, but Israel wants to make sure I watch it. An assistant slips the tape into the vcr, Israel presses the remote, and we all stare at the screen:
1977: An 11-year-old girl named Caroline arrives at the school strapped down onto a stretcher, her head encased in a helmet. In the next shot, free from restraints, she crouches down and tries to smash her helmeted head against the floor.
1981: Janine, also 11 years old, shrieks and slams her head against the ground, a table, the door. Bald spots testify to the severity of her troubles; she’s yanked out so much hair it’s half gone.
Both girls exhibit autistic behaviors, and compared with these scenes, the “After” footage looks almost unbelievable: Janine splashes in a plastic pool, while Caroline grins as she sits in a chair at a beauty salon. “Most people haven’t seen these pictures,” Israel says, setting down the remote. “They haven’t seen children like this, so they cannot imagine. These are children for whom positive-only procedures did not work, drugs did not work. And if it wasn’t for this treatment, some of these people would not be alive.” The video is extremely persuasive: The girls’ self-abuse is so violent and so frightening that it almost makes me want to grab a ged remote and push the button myself. Of course, this is precisely the point.
Considering how compelling the “After” footage is, I am surprised to learn that five of the six children featured in it are still here. “This is Caroline,” one of my escorts says an hour or two later as we walk down a corridor. Without an introduction, I would not have known. Caroline, 39, slumps forward in a wheelchair, her fists balled up, head covered by a red helmet. “Blow me a kiss, Caroline,” Israel says. She doesn’t respond.
A few minutes later, I meet 36-year-old Janine, who appears in much better shape. She’s not wearing a helmet and has a full head of black hair. She’s also got a backpack on her shoulders and canvas straps hanging from her legs, the telltale sign that electrodes are attached to both calves. For 16 years—nearly half her life—Janine has been hooked up to Israel’s shock device. A couple years ago, when the shocks began to lose their effect, the staff switched the devices inside her backpack to the much more painful ged-4.
Rogue Science
In 1994, matthew israel had just 64 students. Today he has 234. This astonishing rate of growth is largely the result of a dramatic change in the types of students he takes in. Until recently, nearly all were “low functioning,” autistic and mentally retarded people. But today slightly more than 50 percent are “high functioning,” with diagnoses like add, adhd, and bipolar disorder. New York state supplies the majority of these students, many of whom grew up in the poorest parts of New York City. Yet despite this change in his population, Israel’s methods have remained essentially the same.
Israel has long faced criticism that he has not published research about his use of electric shocks in peer-reviewed journals, where experts could scrutinize it. To defend his methods, he points to a bibliography of 110 research articles that he’s posted on the Rotenberg Center website. This catalog seems impressive at first. Studied more closely, however, it is not nearly so convincing. Three-quarters of the articles were published more than 20 years ago. Eight were written or cowritten by Lovaas, the ucla-affiliated behaviorist. One of America’s leading autism experts, Lovaas long ago stopped endorsing painful aversives. And Lovaas’ old studies focus primarily on children with autism who engage in extreme self-injury—not on troubled teens who have been diagnosed with adhd or add.
But then, it would be hard for Israel to find contemporary research supporting his program, because the practice of treating self-abusive kids with pain has been largely abandoned. According to Dr. Saul Axelrod, a professor at Temple University and an expert on behavior modification, “the field has moved away from painful stimuli because of public outcry and because we’ve devised better techniques,” including determining the cause of an individual’s self-abuse.
Another expert Israel cites several times is Dr. Brian A. Iwata, a consultant on the development of sibis, the device Israel modified to create his ged. Now a professor of psychology and psychiatry at the University of Florida, he’s a nationally recognized authority on treating severe self-abuse among children with developmental disabilities. Iwata has visited the Rotenberg Center and describes its approach as dangerously simplistic: “There appears to be a mission of that program to use shock for problem behaviors. It doesn’t matter what that behavior is.” Iwata has consulted for 25 states and says there is little relationship between what goes on at Israel’s program and what goes on at other facilities. “He may have gotten his Ph.D. at Harvard, but he didn’t learn what he’s doing at Harvard. Whatever he’s doing, he decided to do on his own.”
Paul Touchette, who also studied with B.F. Skinner, has known Israel since the 1960s when they were both in Cambridge. Like Israel, Touchette went on to treat children with autism who exhibit extreme self-abuse, but he isn’t a fan of Israel’s approach either. “Punishment doesn’t get at the cause,” says Touchette, who is on the faculty of the University of California-Irvine School of Medicine. “It just scares the hell out of patients.”
Over the decades, Touchette has followed Israel’s career and bumped into him at professional conferences. “He’s a very smart man, but he’s an embarrassment to his profession,” Touchette says. “I’ve never been able to figure out if Matt is a little off-kilter and actually believes all this stuff, or whether he’s just a clever businessman.”
Big Reward Store
At the rotenberg center, an elaborate system of rewards and punishments governs all interactions. Well-behaved kids can watch TV, go for pizza, play basketball. Students who’ve earned points for good behavior visit a store stocked with dvd players, cds, cologne, PlayStation 2, Essence magazine, knockoff Prada purses—anything the staff thinks students might want. But even more prized is a visit to the “Big Reward Store,” an arcade full of pinball machines, video games, a pool table, and the most popular feature, a row of 42-inch flat-screen TVs hooked up to Xbox 360s.
Students like the “brs” for another reason—it’s the only place many can socialize freely. At the Rotenberg Center, students have to earn the right to talk to each other. “We had to wait until we were in brs to communicate with others,” says Isabel Cedeño, a 16-year-old who ran away from Rotenberg in 2006 after her boyfriend, a former student, came and got her. “That was the only time you really laughed, had fun, hung around with your friends. Because usually, you can’t talk to them. It was basically like we had to have enemies. They didn’t want us to be friendly with nobody.”
Students live grouped together in homes and apartments scattered in nearby towns and are bused to the facility’s headquarters every morning. They spend their days in classrooms, staring at a computer screen, their backs to the teacher. They are supposed to teach themselves, using self-instruction programs that include lessons in math, reading, and typing. Even with breaks for gym and lunch, the days can be incredibly dull. “On paper, it does look like they’re being educated, because we have lesson plans,” says former teacher Jessica Croteau, who oversaw a classroom of high-functioning teens for six months before leaving in 2006. But “to self-teach is not exciting. Why would the kids want to sit there and read a chapter on their own without any discussion?”
Croteau says teachers have to spend so much time monitoring misbehaviors there’s often little time left for teaching. Whenever a student disobeys a rule, a staff member must point it out, using the student’s name and just one or two rote phrases like, “Mark, there’s no stopping work. Work on your task, please.” Each time a student curses or yells, a staffer marks it on the student’s recording sheet. Teachers and aides then use the sheet to calculate what level of punishment is required—when to just say “No!” and when to shock.
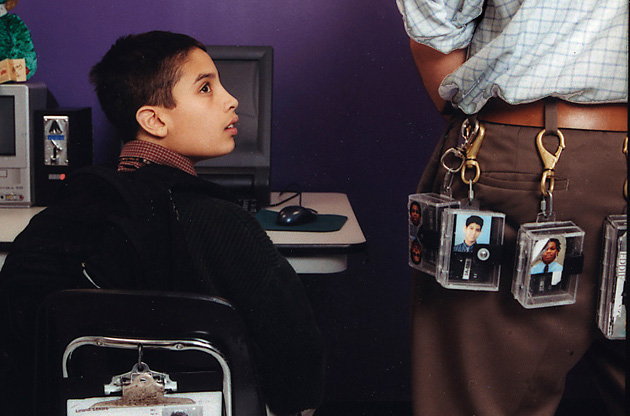
Employees carry students’ shock activators inside plastic cases, which they hook onto their belt loops. These cases are known as “sleds,” and each sled has a photo on it to ensure employees don’t zap the wrong kid.
Behaviorism would seem to dictate that staff shock students immediately after they break the rules. But if employees learn about a misbehavior after it has occurred—by, say, reviewing surveillance footage—they may still administer punishment. Rob Santana recalls that Mondays were always the most stressful day of the week. He would sit at his desk all day, trying to remember if he had broken any rules over the weekend, waiting to see if he’d be shocked.
Employees are encouraged to use the element of surprise. “Attempt to be as discreet as possible and hold the transmitter out of view of the student,” states the employee manual. This way, students cannot do anything to minimize the pain, like flipping over their electrodes or tensing their muscles. “We hear the sound of [a staffer] picking up a sled,” says Isabel, the former student. “Then we turn around and see the person jump out of their seat.”
Employees shock students for a wide range of behaviors, from violent actions to less serious offenses, like getting out of their seats without permission. In 2006, the New York State Education Department sent a team of investigators, including three psychologists, to the Rotenberg Center, then issued a scathing report. Among its many criticisms was that the staff shocked kids for “nagging, swearing, and failing to maintain a neat appearance.” Israel only disputes the latter. As for nagging and swearing? “Sometimes a behavior looks innocuous,” he says, “but if it’s an antecedent for aggression, it may have to be treated with an aversive.”
New York officials disagreed, and in January 2007 issued regulations that would prohibit shocking New York students for minor infractions. But a group of New York parents filed a federal lawsuit to stop the state from enforcing these regulations. They prevailed, winning a temporary restraining order against the state, one that permits the Rotenberg Center staffers to continue using shock. The parents’ case is expected to go to trial in 2008.
When they talk about why they use the shock device, Israel and his employees like to use the word “treatment,” but it might be more accurate to use words like “convenience” or “control.” “The ged—it’s two seconds and it’s done,” says Patricia Rivera, a psychologist who serves as assistant director of clinical services. “Then it’s right back to work.” By contrast, it can take 8 or 10 employees half an hour or longer to restrain a strong male student: to pin him to the floor, wait for him to stop struggling, then move his body onto a restraint board and tie down each limb. Restraining five or eight kids in a single day—or the same student again and again—can be incredibly time-consuming and sometimes dangerous.
Even with the ged, the stories both students and employees tell make the place sound at times like a war zone: A teenage boy sliced the gym teacher across the face with a cd. A girl stabbed a staffer in the stomach with a pencil. While staff have been contending with injuries ever since Israel opened his facility, the recent influx of high-functioning students, some with criminal backgrounds, has brought a new fear: that students will join forces and riot. Perhaps tellingly, among high-functioning kids most of the violence is directed at the staff, not each other.
“Our Students Have a Tendency to Lie”
Rotenberg staff place the more troubled (or troublesome) residents on 1:1 status, meaning that an aide monitors them everywhere they go. For extremely violent students, the ratio is 2:1. Soon after I arrived, right before I set off on my tour, a small crowd gathered—it seemed that almost the entire hierarchy of the Rotenberg Center was going to follow me around. That’s when I realized I’d been put on 5:1. As I began to roam around the school with my escorts, my every move monitored by surveillance cameras, I realized it would be impossible to have a private conversation with any student. The best I could hope for would be a few unscripted moments.
Ten years ago, a reporter visiting Israel’s center would have been unable to talk to most students; back then few of them could speak. These days, there are more than 100 high-functioning kids fully capable of voicing their views, and Israel has enlisted a few in his campaign to promote the ged. “If we had only [severely] autistic students, they couldn’t talk to you and say, ‘Gee, this is really helping me,'” Israel says. “Now for the first time we have students like Katie who can tell you it helped them.”
In the world of the Rotenberg Center, Katie Spartichino is a star. She left the facility in the spring of 2006 and now attends community college in Boston. Around noon, a staff member brings her back to the facility to talk to me. We sit at an outdoor picnic table away from the surveillance cameras but there’s no privacy: Israel and Karen LaChance, the assistant to the executive director for admissions, sit with us.
Katie, 19, tells me she overdosed on pills at 9, spent her early adolescence in and out of psych wards, was hooked up to the ged at 16, and stayed on the device for two years. “This is a great place,” she says. “It took me off all my medicine. I was close to 200 pounds and I’m 160 now.” She admits her outlook was less rosy when she first had to wear the electrodes. “I cried,” she says. “I kind of felt like I was walking on eggshells; I had to watch everything I said. Sometimes a curse word would just come out of my mouth automatically. So being on the geds and knowing that swearing was a targeted behavior where I would receive a [GED] application, it really got me to think twice before I said something disrespectful or something just plain-out rude.”
As Katie speaks, LaChance runs her fingers through Katie’s hair again and again. The gesture is so deliberate it draws my attention. I wonder if it’s just an expression of affection—or something more, like a reward.
“Do you swear anymore?” I ask.
“Oh, God, all the time,” Katie says. She pauses. “Well, I have learned to control it, but I’m not going to lie. When I’m on the phone, curse words come out.”
The hair stroking stops. LaChance turns to Katie. “I hope you’re not going to tell me you’re aggressive.”
“Oh, no, that’s gone,” Katie says. “No, no, no. The worst thing I do sometimes is me and my mom get into little arguments.”
For Israel, of course, one drawback of having so many high-functioning students is that he cannot control everything they say. One afternoon, when I walk into a classroom of teenagers, a 15-year-old girl catches my eye, smiles, and holds up a sheet of paper with a message written in pink marker: HELP US. She puts it back down and shuffles it into her stack of papers before anyone else sees. When I move closer, she tells me her name is Raquel, she is from the Bronx, and she wants to go home.
My escorts allow me to interview Raquel while two of them sit nearby. Raquel is not hooked up to the ged, but she has many complaints, including that she has just witnessed one of her housemates get shocked. “She was screaming,” Raquel says. “They told her to step up to be searched; she didn’t want to step up to be searched, so they gave her one.” After 20 minutes, my escorts cut us off. “Raquel, you did a great job—thank you for taking the time,” says Patricia Rivera, the psychologist.
Once Raquel is out of earshot, Rivera adds, “Some of the things she said are not true, some of them are. Our students obviously have a tendency to lie about things.” She explains that a staff member searches Raquel’s housemate every hour because she’s the one who recently stabbed an employee with a pencil.
The Rotenberg Center does not have a rule about how old a child must be before he or she can be hooked up to the ged. One of the program’s youngest students is a nine-year-old named Rodrigo. When I see him, he is seated outside at a picnic table with his aide. Rodrigo’s backpack looks enormous on his tiny frame; canvas straps dangle from both legs.
“He was horrible when he first came in,” Rivera says. “It would take five staff to restrain him because he’s so wiry.” What was he like? “A lot of aggression. A lot of disruptive behavior. Whenever he was asked to do a task that he didn’t feel like doing, he would scream, yell, swear. The stuff that would come out of his mouth you wouldn’t believe—very sexually inappropriate.”
“Rodrigo, come here,” one of my escorts says.
Rodrigo walks over, his straps slapping the ground. He wears a white dress shirt and tie—the standard uniform for male students—but because he is so small, maybe 4 feet tall, his tie nearly reaches his thighs. “What’s that?” he asks.
“That’s a tape recorder,” I say. “Do you want to say something?”
“Yeah.”
Unfazed by the presence of Israel, Rivera, and my other escorts, Rodrigo lifts a small hand and pulls the recorder down toward his lips. “I want to move to another school,” he says.
The Employee-Modification System
To understand how the Rotenberg Center works, it helps to know that it runs not just one behavior-modification program, but two—one for the residents, and one for the staff. Employees have no autonomy. If a staffer believes it’s okay to shock a kid who is smashing his head against a wall, but it’s not okay to shock someone for getting out of his chair without permission, that could spell trouble. “There’s pressure on you to do it,” a former teacher told me. “They punish you if you don’t.”
I met this former teacher at a restaurant, and our meeting stretched on for six hours. At times it felt less like an interview than a confession. “The first time you give someone a ged is the worst one,” the teacher said. “You don’t want to hurt somebody; you want to help. You’re thinking, ‘This has got to be okay. This has got to be legal, or they wouldn’t be doing this.'” At the Rotenberg Center, it’s virtually impossible to discuss such concerns with coworkers because there are cameras everywhere, even in the staff break room. Staff members who want to talk to each other without being overheard may meet up in the parking lot or scribble notes to each other. But it’s hard to know whom to trust, since Israel encourages employees to file anonymous reports about their coworkers’ lapses.
In addition, staff members are prohibited from having casual conversations with each other. They cannot, for example, say to a coworker, “Hey, did you see the Red Sox game last night?” “We don’t want them discussing their social life or the ball games in front of the students or while they’re on duty,” Israel says. “So we’ll sometimes actually have one staffer deliberately start a social conversation with another and we’ll see whether the other—as he or she should—will say, ‘I don’t want to discuss that now.'” Monitors watch these setups on the surveillance cameras and punish staffers who take the bait.
Former employees describe a workplace permeated with fear—fear of being attacked by students and fear of losing their job. There are so many rules—and so many cameras—it’s not easy to stay out of trouble. Employees quit or are fired so often that two-thirds of the direct-care employees remain on the job for less than a year.
New employees must sign a confidentiality agreement promising not to talk about the Rotenberg Center—even after they no longer work there. Of the eight ex-employees I interviewed, most did not want to be identified by name for fear of Israel suing them; all were critical of how the ged is used. Maybe, says one, the use of shocks was justified in a few extreme self-injurious cases, but that’s all. “Say you had a hospital that was the only hospital in the nation that had chemotherapy, and they were treating people who had the common cold with it,” she says. “I think the extreme to which they abuse their power has outweighed what good they do.”
The Hard Lessons of Connie Chung
Matthew Israel has been fielding questions from journalists since the 1970s, but few have examined his operation as thoroughly—and critically—as the producers at Eye to Eye with Connie Chung did. In 1993, they spent six months investigating the facility. They even found an employee willing to go inside with a hidden camera. But Israel ended up getting the last laugh. As he recounts the story for me, he can barely contain his glee. “We refused to meet with her unless the parents could be in the same room,” he says, grinning. “She talked to the parents, and they really gave it to her.” This is no exaggeration: When Chung tried to ask him tough questions, his parent-supporters shouted her down.
Throughout this raucous meeting, Israel had his own camera rolling, too, which turned out to be a brilliant move. Before cbs got its 40-minute story on the air, Israel launched a national campaign to discredit both Chung and her report. He accused her of being “biased” and “hostile,” and to prove it, he distributed edited videotapes of her interview to media critics and cbs affiliates. It worked. A New York Times television critic savaged cbs, accusing it of using “shabby tricks of the trade.” Suddenly the story was not about whether the school had abused students—but whether cbs had abused the school.
“I don’t think it was a positive thing for her career,” says Israel, still smiling. It’s late in the day, right near the end of my visit, and I’m starting to wonder why he’s brought up this topic.
By now I’ve spent 22 hours with Israel and his staff—wandering around the facility, meeting parents they’ve brought in for me to interview. But before I depart, there’s one more place I want to see, the room where they repair the geds. Israel and Glenda Crookes, an assistant executive director, agree to take me there. It is just past 7 p.m. and drizzling as we climb into Israel’s Lexus for a short drive to the maintenance building.
There, Crookes and Israel lead me down a hall, past storerooms filled with red helmets, ged sleds, batteries and their chargers. The room at the end of the hall looks like it could be a repair shop for any sort of electronics equipment: scissors, screwdrivers, industrial-grade glue, a Black & Decker Pivot Driver. On one desk, I spot a form called a ged Trouble Report. The report explains that someone dropped off Duane’s shock device because it was “making rattling noises.” Crookes explains, “Anytime a screw is loose or anything is wrong with the device, it’s automatically sent back here.”
A Trouble Report on another desk suggests a more serious problem: “Jamie Z was getting his battery changed, Luigi received a shock.” “What does this mean?” I ask. Crookes picks up the paper, reads it, then hands it to Israel and walks away. Her gesture seems to say, I cannot believe we just spent two days with this reporter and now this is the last thing she sees.
Israel stares at the report, then reaches into his pocket and pulls out a pair of reading glasses. Nobody says anything. Outside, one car after another races by, the tail end of the evening commute.
After a minute or two, Israel says, “Well, I don’t understand the whole of it.” He is still staring at the paper in his hand. “But there was apparently a spontaneous activation.” The ged, in other words, delivered a shock without anyone pressing its remote.
This moment reminds me of something Israel told me earlier about the premise of Skinner’s Walden Two, that by changing people’s behaviors you can help them have a better life. But, Israel was careful to add, “The notion was that you needed to have the whole environment under control. With a school like this, we have an awful lot. Not the whole environment, but an awful lot.”
He was right; he controls nearly every aspect of his facility. But all of his surveillance cameras and microphones and paperwork and protocols had failed to protect Luigi, a mentally retarded resident who had done nothing wrong.