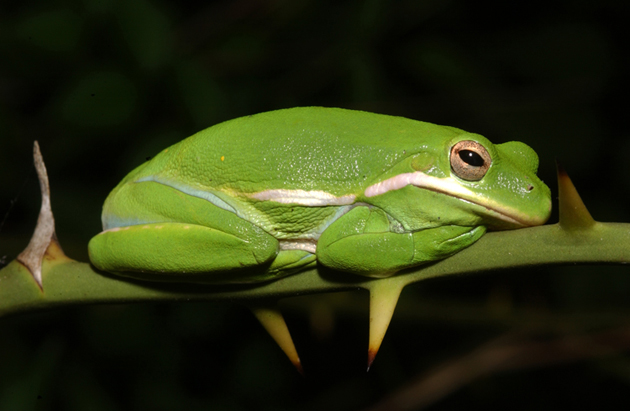
Green tree frog (Hyla cinerea)Credit: Stephen Tilley
If you live near water in the American Southeast, you may have run across the green tree frog—or at least heard the species as it croaks (in a sound that kind of resembles rapid fire quacking). It’s a small frog that’s often found in pet stores. It’s the state amphibian of Louisiana and Georgia. And it’s one of many species of amphibians, reptiles, birds and even mammals that may be incapable of evolving fast enough to keep up with what global warming has in store.
That’s the upshot of a new study in the journal Ecology Letters, whose authors used a vast body of data on 540 separate species’ current climatic “niches,” and their evolutionary histories of adapting to different conditions, to determine whether they can evolve fast enough to keep up with the changing climate. More specifically, the study examined “climatic niche evolution,” or how fast organisms have adapted to changing temperature and precipitation conditions in their habitats over time.
Under normal circumstances, the answer is very slowly. On average, the study found that animals adapted to temperature changes at a rate of less than 1 degree Celsius (or 1.8 degrees Fahrenheit) per million years. By contrast, global warming is expected to raise temperatures on the order of 4 degrees Celsius (or 7.2 degrees Fahrenheit) in the next 100 years.
“It seems like climate change is too fast, relative to how quickly the climatic niches of species typically evolve,” explains evolutionary biologist John Wiens of the University of Arizona, who conducted the research along with a colleague at Yale University.
Take the green tree frog. According to data provided by Wiens, the annual mean temperature in the species’ range across the Southeast is about 66 degrees Fahrenheit. For its closely related “sister” species the barking tree frog, meanwhile, it’s 65.3 degrees. The two species diverged some 13.4 million years ago, and their common ancestor is estimated to have lived in mean climatic conditions somewhere in between these two numbers, at 65.5 degrees.
The rate of evolutionary change in response to temperatures for these frogs is therefore extremely slow—”about 100,000 to 500,000 times slower than the expected rate of climate change within the range of the species from 2010 to 2100,” Wiens says.
Even if you take a species that evolved much more rapidly in relation to changing temperatures, the conclusion remains the same. The species still didn’t change fast enough in the past for scientists to think that it can evolve to keep up with global warming in the future.
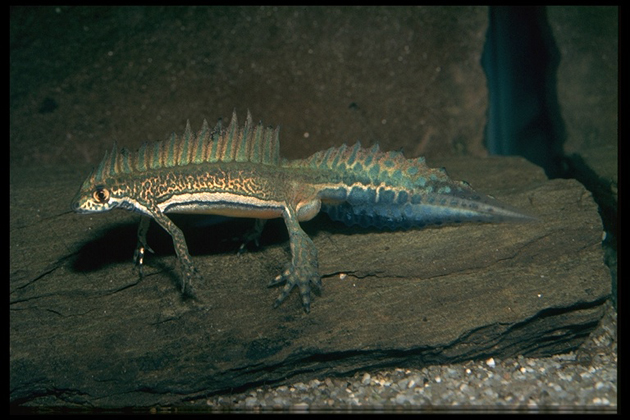

An example of a faster evolving species would be the Northern banded newt, which lives at relatively high altitudes in a range that spans from Russia to Turkey. Annual mean temperatures in its habitat are about 50.4 degrees Fahrenheit; but for a closely related species, the Southern banded newt, the average temperature is vastly different—65.7 degrees. The two species’ common ancestor is estimated to have lived only 350,000 years ago, amid mean temperatures of about 59.5 degrees. Adaptation to new climatic conditions among these newts thus happened much faster than among tree frogs—“but still about 1,600 to 4,700 times slower” than the kind of changes we expect from global warming, according to Wiens.
In the new paper, Wiens and his coauthor apply a similar analysis to several hundred other species, ranging from cranes and crocodiles to hawks and turtles. And none adjusted to temperatures in the evolutionary past at anything like the rate at which temperature change is now coming.
This does not mean that each and every species will go extinct. Some may shift their ranges to keep up with favorable temperatures. Some may perish in certain locales but not others. And some may find a means of coping in a changed environment. Just because these species have never experienced what climate change is about to throw at them doesn’t prove that they’re incapable of surviving it.
Nonetheless, the new research as a whole validates a striking statement made recently by the renowned climate scientist Michael Mann of Penn State University. At a Climate Desk Live event in May, Mann remarked that there is “no evidence” from the planet’s past to suggest that life can adapt to changes as rapid as the ones we’ve now set in motion.
Wiens’ data add an exclamation point to Mann’s statement. And it also raises an unavoidable question: What is going to happen to the species responsible for all of this, namely, humans?
“Humans will be fine,” says Wiens, “because we have things like clothes and air conditioning.”