Maybe not as effective as you think.Courtesy <a href="http://www.planbonestep.com/news-and-media.aspx">Teva Pharmaceutical Industries</a>
Update (11/25/13): An FDA spokeswoman tells Mother Jones the agency is evaluating whether to require US emergency contraceptive pill makers to change their labels.
The European manufacturer of an emergency contraceptive pill identical to Plan B, also known as the morning-after pill, will warn women that the drug is completely ineffective for women who weigh more than 176 pounds and begins to lose effectiveness in women who weigh more than 165 pounds. HRA Pharma, the French manufacturer of the European drug, Norlevo, is changing its packaging information to reflect the weight limits. European pharmaceutical regulators approved the change on November 10, but it has not been previously reported.
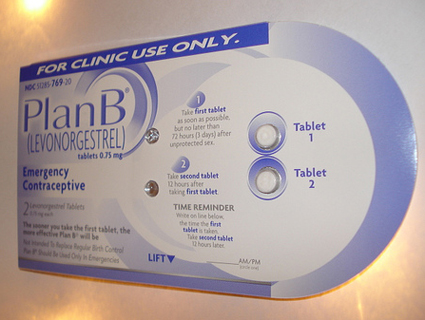
This development has implications for American women. Some of the most popular emergency contraceptive pills sold over the counter in the United States—including the one-pill drugs Plan B One-Step, Next Choice One Dose, and My Way, and a number of generic two-pill emergency contraceptives—have a dosage and chemical makeup identical to the European drug. Weight data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) suggests that, at 166 pounds, the average American woman is too heavy to use these pills effectively.
These pills, which use a compound called levonorgestrel to prevent pregnancies, are the most effective morning-after pills available without a prescription. Other pills sold in the United States require a prescription, are less effective at preventing pregnancy, or cause side effects such as nausea or vomiting. Plan B One-Step, which retails for $50, is the only emergency contraceptive drug in the United States available to women of all ages without a prescription.
Emergency contraception advocates reacted to the news about Norlevo with dismay. “There’s a whole swath of American women for whom [these pills] are not effective,” says James Trussell, a professor of public affairs at Princeton and a senior fellow with the Guttmacher Institute, a think tank for reproductive health issues.
Data for the years 2007 to 2010 show the average weight of American women 20 years and older is 166.2 pounds—greater than the weight at which emergency contraceptive pills that use levonorgestrel begin to lose their effectiveness. The average weight of non-Hispanic black women aged 20 to 39 is 186 pounds, well above the weight at which these pills are completely ineffective. A CDC survey published in February found that 5.8 million American women used emergency contraceptive pills from 2006 to 2010.
HRA Pharma began investigating the need to change Norlevo’s label after Anna Glasier, a professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Edinburgh, published research in 2011 showing emergency contraceptive pills that use levonorgestrel are prone to fail in women with a higher body mass index. In an email, Karina Gajek, a spokeswoman for HRA Pharma, says that by December 2012, the company had reviewed clinical data on its own and requested permission from a European Union governing body to update its product information.
New leaflets warning women about the weight limits will appear in every box of Norlevo sold in Europe in the first half of 2014. The new packaging slip will read, in part: “Studies suggest that Norlevo is less effective in women weighing [165 pounds] or more and not effective in women weighing [176 pounds] or more” and that Norlevo “is not recommended…if you weigh [165 pounds] or more.”
But American manufacturers do not currently advise American customers of weight limits for levonorgestrel-based emergency contraceptives.
Because the Food and Drug Administration prohibits generic drug manufacturers from changing product information unless the brand name manufacturer makes a change, companies that manufacture generic versions of Plan B One-Step cannot update their packaging information unless Teva Pharmaceutical Industries, the exclusive manufacturer of Plan B One-Step, acts first. (The FDA has proposed a rule change that would allow generic manufacturers to update drug information independently.) A spokeswoman for Teva declined to comment for this article.
It is not clear whether drugmakers can formulate an effective levonorgestrel pill for women who weigh more than 165 pounds. “A dose increase of levonorgestrel is not proven to be a solution for this problem,” notes Gajek, the HRA Pharma spokeswoman. “However, women with higher weight are advised to discuss alternative emergency contraceptive options with their physician: IUD or alternative oral emergency contraceptive.” In the United States, IUD insertion can cost anywhere from $500 to $900.
According to a database of emergency contraceptive pills maintained by Princeton, HRA Pharma sells Norlevo throughout most European countries, parts of China, parts of the Middle East, many Francophone African countries, Australia, Taiwan, and South Korea. Norlevo was also recently approved for sale in India. Gajek says that changes to Norlevo’s labels will be “procedure and country-dependent” and adds that the company has no timetable for changing its product labels in non-European countries.
A spokesman for Gavis, which manufactures the Plan B One-Step generic called My Way, declined to comment for this story. Actavis, which makes Next Choice One Dose, did not reply to requests for comment.