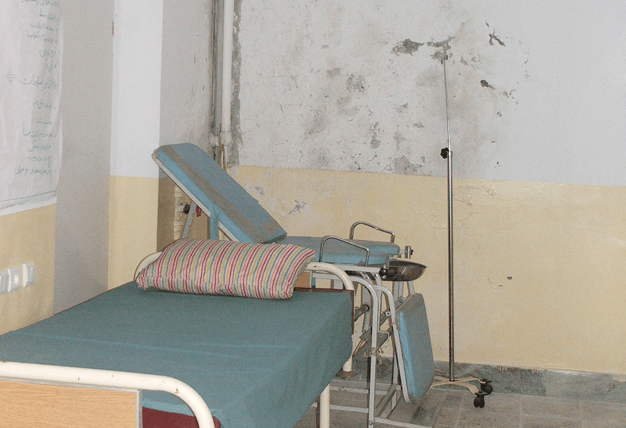
A US soldier from the 101st Airborne Division destroys opium poppies growing in a field in Khost province, Afghanistan, in 2008.Rafiq Maqbool/AP
Opium poppy cultivation in Afghanistan is at record levels, according to a new report from the Office of the Special Inspector General for Afghanistan Reconstruction. That’s despite more than a decade of American efforts to knock out the Afghan drug trade—at a cost of roughly $7.6 billion.
SIGAR’s data, which comes from the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC), shows that Afghan opium cultivation nearly tripled between 1994 and 2013. More than 780 tons of heroin or morphine could be produced with the current crop, whose total value is estimated at nearly $3 billion, up from $2 billion in 2012.
In his report, John F. Sopko, the Special Inspector General for Afghanistan Reconstruction, informs Secretary of State John Kerry, Attorney General Eric Holder, and USAID administrator Rajiv Shah that the levels of opium poppy production don’t exactly square with all the time, money, and effort that have gone into eradicating crop. “The recent record-high level of poppy cultivation calls into question the long-term effectiveness and sustainability of [prior US government and coalition] efforts,” Sopko writes. “Given the severity of the opium problem and its potential to undermine U.S. objectives in Afghanistan, I strongly suggest that your departments consider the trends in opium cultivation and the effectiveness of past counternarcotics efforts when planning future initiatives.”
Afghanistan produces more than 80 percent of the world’s illicit opium. SIGAR reports that much of the 494,000 acres of newly arable land in southwest Afghanistan—created by a boom in affordable deep-well technology—”is dedicated to opium cultivation.”
In the State Department’s and USAID’s joint response to the report, Charles Randolph, a program coordinator at the US Embassy in Kabul, agrees with many of Sopko’s observations. Randolph concedes that the situation is “disappointing, as was the decline in poppy eradication by provincial authorities this year.”
Randolph notes that the opium trade has undermined the government in Kabul and helped the Taliban and other insurgents. “The narcotics trade has also been a windfall for the insurgency, which profits from the drug trade at almost every level,” he writes.
But, he adds, the United States and its Afghan counterparts have had some success with approaches such as special interdiction units and drug treatment programs. “There is no silver bullet to eliminate drug cultivation or production in Afghanistan or to address the epidemic of substance abuse disorders that plagues too many Afghans,” he writes.
The Department of Defense, in its official response to SIGAR, says it does not conduct poppy eradication activities in Afghanistan, and points the finger at Kabul. “The failure to reduce poppy cultivation and increase eradication is due to the lack of Afghan government support for the effort,” writes Michael D. Lumpkin, the assistant secretary of defense for special operations/low-intensity conflict. “Poverty, corruption, the terrorism nexus to the narcotics trade, and access to alternative livelihood opportunities that provide an equal or greater profit than poppy cultivation are all contributors to the Afghan drug problem.”
Drug addiction is a major problem in Afghanistan, with as many 1 million people addicted to opium, heroin, and other drugs—including children as young as four. In a joint statement that prefaced the release of the 2013 data, Din Mohammad Mobariz Rashidi, Afghanistan’s acting minister of counternarcotics, and Yury Fedotov, the executive director of the UNODC, said that Afghan and American officials are making progress, and that authorities seize roughly 10 percent of Afghan poppy production. But, they continued, not enough “powerful figures” are being prosecuted. That could be a reference to former Afghan president Hamid Karzai’s brother, who was accused of having strong connections to the Afghan heroin trade.
“In order to be successful and sustainable, counter-narcotics efforts must finally break out of their insular, silo approach,” the pair wrote. “If the drug problem is not taken more seriously by aid, development and security actors, the virus of opium will further reduce the resistance of its host, already suffering from dangerously low immune levels due to fragmentation, conflict, patronage, corruption and impunity.”