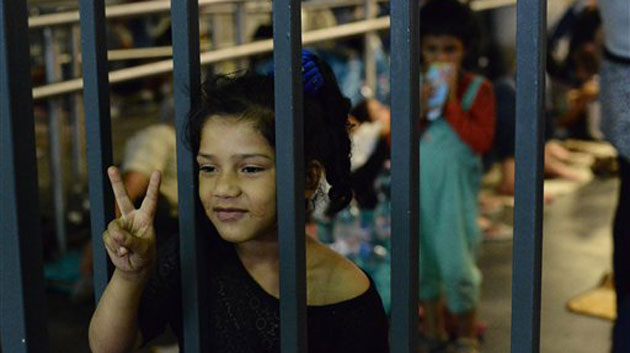Syrian refugees arrive at the Athens' port of Piraeus on September 1.Thanassis Stavrakis/AP
With the refugee crisis in Europe worsening dramatically, the Obama administration announced on Thursday that it would accept at least 10,000 Syrian refugees in the next year. That’s a significant step: Over the past four years, as millions of Syrians have been displaced by a brutal civil war, the United States has admitted only about 1,500 Syrian refugees. But humanitarian advocates say President Barack Obama’s move doesn’t go nearly far enough.
The US offer “is cold comfort to the victims of the Syrian conflict,” said International Rescue Committee president David Miliband in a press release Friday. “With 4 million living in limbo and tens of thousands making desperate choices to reach safety, the US has a moral responsibility to lead and is fully equipped to respond in a far more robust way.” Part of the solution, experts argue, is for the United States to help organize a program to send refugees to developed countries around the world. After all, they point out, we’ve done it before.
“This is not science fiction,” said Francois Crepeau, the United Nations’s special rapporteur for the human rights of migrants. “We resettled almost 2 million Indochinese 40 years ago. We can do it again.”
After the end of the Vietnam War, hundreds of thousands of people attempted to flee Southeast Asia, mostly from Vietnam, by riding rickety, overloaded boats to nearby countries. Those countries, like many European countries during the current crisis, felt overwhelmed by the unyielding and disorganized flow of people arriving on their shores. They eventually announced that they would refuse to take in any more “boat people,” prompting the international community to create a global resettlement program with the help of the UN High Commissioner for Refugees. The UNHCR ultimately resettled 1.3 million Southeast Asians in countries around the world, including more than 800,000 in the United States.
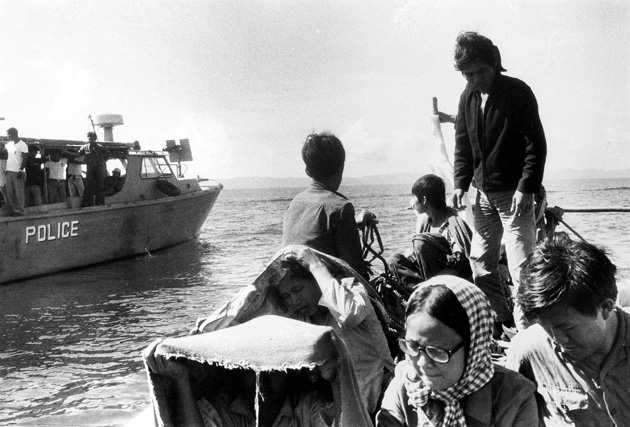
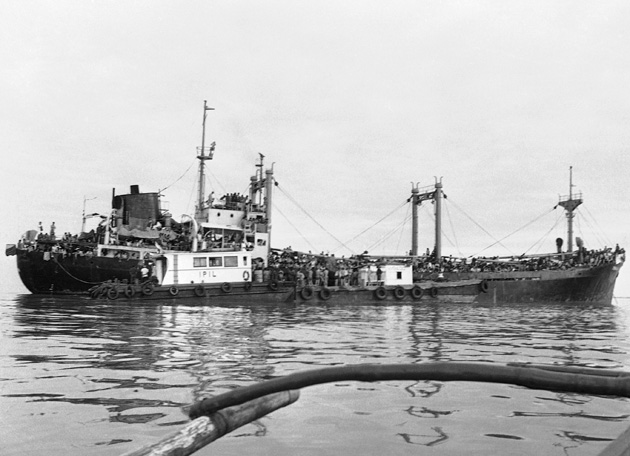


Two million is now about the number that Crepeau thinks should be resettled today across the “global north”—essentially the European Union, plus the United States, Canada, Australia, and New Zealand. “Two million refugees resettled over five years means 400,000 per year,” he said. “Four hundred thousand per year divided by 32 countries representing 850 million inhabitants is not much.”
That’s still a small fraction of the nearly 12 million people exiled or internally displaced by the war in Syria, not to mention the significant number of people fleeing violence in Afghanistan and Iraq or repression in Eritrea and other countries. “It’s going to be a small percentage. I don’t see any way it’s not going to be that,” acknowledged Larry Yungk, a senior resettlement officer with the UNHCR. “That being said, we have always said that we need more resettlement places, whether it’s for Syrians or globally. And the Syrian conflict, I think, has shown why we need more places.”
Finding those places has been particularly difficult in Europe. Yungk praised the “very generous response” of Germany, which expects to take in 800,000 asylum seekers this year, but several other EU countries are openly hostile to accepting refugees. The government of Denmark ran newspaper ads in Lebanon telling Syrian refugees they’re not welcome in the Scandinavian country. Hungary has subjected migrants to humiliating treatment, even as it builds a border fence to stop the influx. Such countries helped block a mandatory refugee quota system for EU members in May, and Germany’s efforts to try again are meeting with little success.
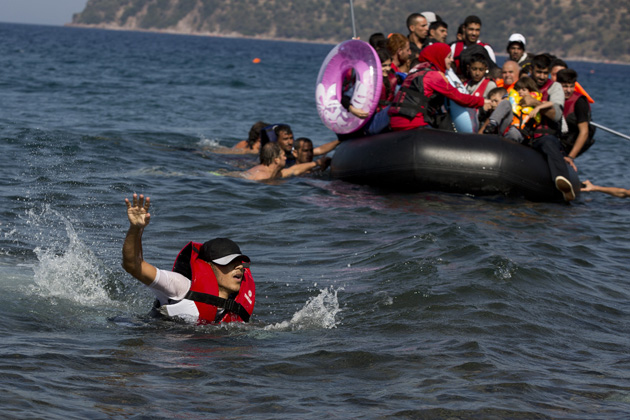

Yungk, who spoke with Mother Jones prior to the administration’s announcement on Thursday, isn’t optimistic that the United States will ultimately admit a dramatically higher number of people for resettlement. Not only is the United States far from the Middle East, where the bulk of the refugees are, but its system for investigating and approving refugees is already heavily taxed. The United States takes in about 70,000 refugees from across the world every year. But the 1,500 Syrians granted refugee status so far are just a small fraction of the 18,000 or so Syrian cases that the UNHCR has submitted to the US government.
“Our goal is to try to work with [the United States] to reduce that gap,” Yungk said. “If we do, then the ability is there to talk, I think, about more referrals. And the United States will be probably more willing to look at it.” The State Department did not respond to a request for comment.
But even if the United States doesn’t accept a large number of refugees—the 10,000 that will now be allowed into the United States is about half the number of refugees who arrived in Munich from Hungary last weekend—merely taking action could help convince other nations to pitch in. “Yes, it would be nice to resettle some more refugees today,” said James Hathaway, the director of the Program in Refugee and Asylum Law at the University of Michigan. “But the important thing that they should be doing is leading—not a new refugee convention, but a new mechanism to share the responsibilities of protection around the world. The US needs to show leadership on that.”
Pressure is growing on the United States to do more. In May, a group of 14 Senate Democrats wrote a letter urging the Obama administration to accept up 65,000 Syrians. A coalition of American groups including the US Conference of Catholic Bishops, the US Committee for Refugees and Immigrants, and the International Rescue Committee is now calling for the United States to take in up to 100,000 Syrians. Even GOP presidential candidate Donald Trump has come out in support of expanded resettlement in the United States. But even if the magnitude of the refugee crisis has prompted some change, large-scale progress will be much harder.
“If you do go back to some of the big situations like Bosnia and Southeast Asia, what you did see is, frankly, a coalition of countries all coming together to say, ‘We’ll do this,'” Yungk said. “So that’s what it would take.”
Max J. Rosenthal is reporting from Berlin as part of the Arthur F. Burns Fellowship, a two-month reporting program in Germany run by the International Center for Journalists. Gabrielle Canon contributed reporting to this article from San Francisco.