One of the cruel ironies of climate change is that its impacts tend to fall hardest on the countries least equipped to manage them.
When drought or sea level rise strike the United States, communities at least have access to federal aid, top scientific expertise, public investment in expensive climate-ready infrastructure, and the like. But some of the most extreme effects of global warming are headed for developing countries—drought wiping out crops in East Africa, or catastrophic hurricanes pounding Southeast Asia—that don’t have access to those resources.
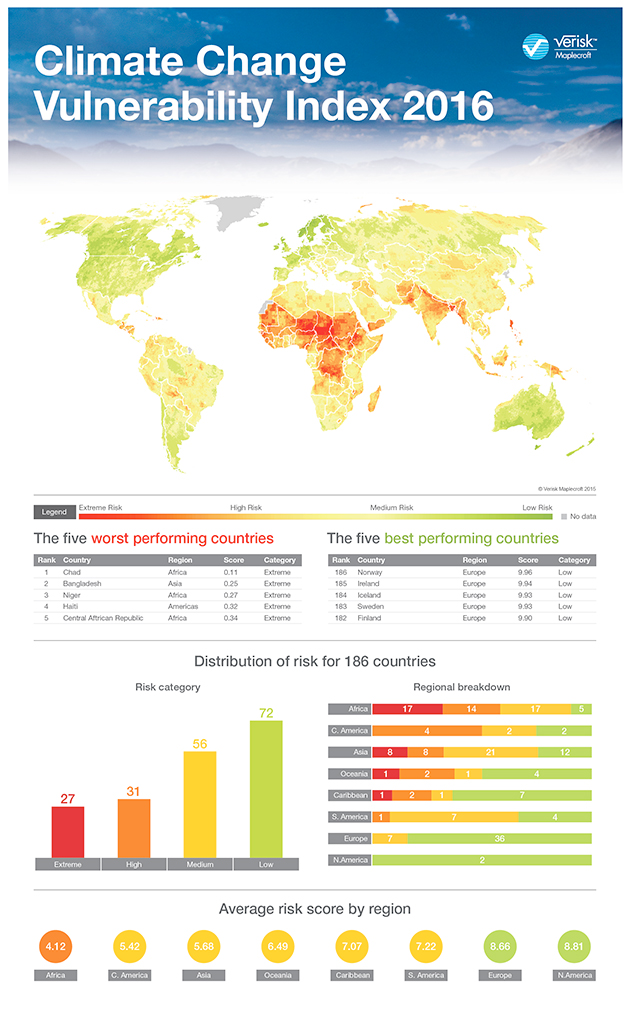
New research from Maplecroft, a UK-based risk consultancy, paints a pictures of where vulnerability to climate change is most pressing. Their analysis drew on three criteria: exposure to extreme events, based on the latest meteorological science; sensitivity to impacts (i.e., does a country have other sources of income and food supply if agriculture takes a hit?); and adaptive capacity—are the country’s government and social institutions prepared to work under adverse climate conditions and help citizens adapt to them?
Unsurprisingly, Africa and Southeast Asia ranked the lowest, while Scandinavian countries ranked the highest. (While definitely at risk from sea level rise, countries such as Norway and Sweden have rich, highly functional governments to manage adaptation.) The major global climate talks in Paris are coming up in just a couple weeks; the chart above makes it clear why it’s so important for big players like the US and China to work closely with delegations from developing countries on solutions that will provide immediate support and relief.