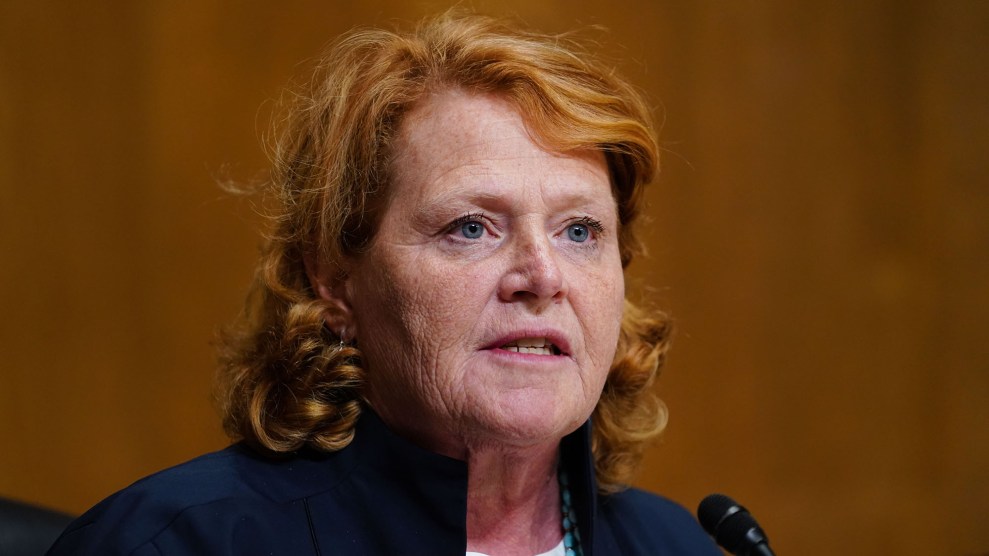
Sen. Heidi Heitkamp (D-N.D.) faces a tougher road to reelection after Tuesday's ruling.Jay Mallin/ZUMA
The Supreme Court on Tuesday upheld a lower-court order requiring voters in North Dakota to present certain forms of identification and proof of their residential address in order to cast a ballot in next month’s elections. A case challenging this requirement on behalf of the state’s sizable Native American populations alleged that the requirement would disenfranchise tribal residents, many of whom lack the proper identification and do not have residential addresses on their identification cards.
The Supreme Court’s order will likely make it harder for Sen. Heidi Heitkamp, considered the most vulnerable Democrat in the Senate, to retain her seat in November. Heitkamp won her seat by less than 3,000 votes in 2012 with strong backing from Native Americans, and she is the only statewide elected Democrat. North Dakota Republicans began changing voting rules to make it harder to cast a ballot months after Heitkamp’s victory six years ago. Republicans have claimed the changes to voter ID requirements are intended to stop voter fraud, even though in-person fraud is exceedingly rare.
Justice Brett Kavanaugh, who was sworn in on Monday, did not partake in the decision, and Justices Ruth Bader Ginsburg and Elena Kagan dissented.
North Dakota’s 2017 voter law ID was challenged by Native residents who alleged that the law disproportionately blocked Native Americans from voting. In April, a federal district court judge blocked large portions of the law as discriminatory against Native voters. “The State has acknowledged that Native American communities often lack residential street addresses,” Judge Daniel Hovland wrote. “Nevertheless, under current State law an individual who does not have a ‘current residential street address’ will never be qualified to vote.” According to the website of the Native American Rights Fund, which represents the plaintiffs, many native residents lack residential street addresses because “the U.S. postal service does not provide residential delivery in these rural Indian communities.”As a result, tribal IDs use P.O. boxes, which are not sufficient under North Dakota’s new law—a specification that seems designed to disenfranchise native voters. Hovland’s ruling was in place during the primaries this spring.
But in September, the 8th Circuit Court of Appeals allowed the law to go into effect. The Supreme Court upheld that ruling Tuesday. In her dissent, Ginsburg argued that the Supreme Court’s order was at odds with one of the top court’s most frequently invoked doctrines on election law: not to change the rules right before an election. By allowing a different set of ID rules in the general election from in the primary, Ginsburg warned, the court was risking widespread confusion and disenfranchisement.
“The risk of voter confusion appears severe here because the injunction against requiring residential-address identification was in force during the primary election and because the Secretary of State’s website announced for months the ID requirements as they existed under that injunction,” Ginsburg wrote. “Reasonable voters may well assume that the IDs allowing them to vote in the primary election would remain valid in the general election. If the Eighth Circuit’s stay is not vacated, the risk of disfranchisement is large.”
Ginsburg noted that according to the factual record of the case, about 20 percent of voters likely to try to cast a ballot in the midterms will lack the required identification. Another “approximately18,000 North Dakota residents also lack supplemental documentation sufficient to permit them to vote without a qualifying ID,” she noted.