<a href="http://www.google.com/imgres?imgurl=&imgrefurl=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.politico.com%2Fnews%2Fstories%2F0912%2F80607.html&h=0&w=0&sz=1&tbnid=0Sp7sCX95Ldq0M&tbnh=165&tbnw=305&zoom=1&docid=NY7tQ8CN1FTNFM&hl=en&ei=GLXmUZm4IOPCigLpmIHgBw&ved=0CAEQsCU">Politico</a>
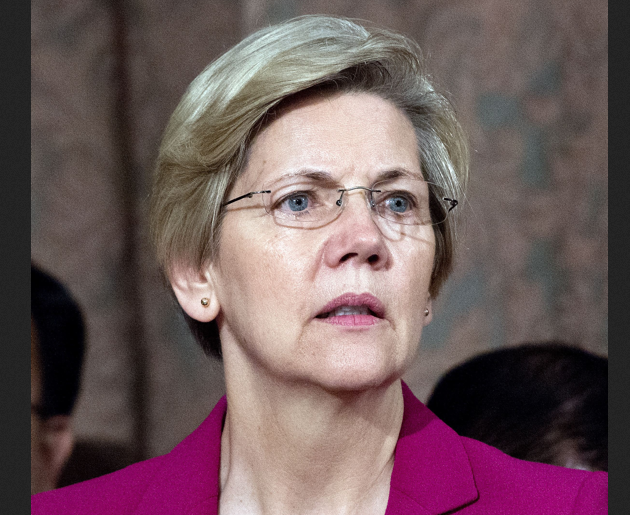
“It is truly a historic day,” Sen. Elizabeth Warren said Tuesday after the Senate agreed to allow a vote on Richard Cordray to head the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB), the consumer watchdog agency that Warren devised and helped get on its feet. “It took nearly two years, but…now the American people will have a strong watchdog in Washington,” Warren continued in a conference call with reporters. “David beat Goliath.”
On Tuesday evening, the Senate confirmed Cordray by a vote of 66 to 34 after Republicans agreed not to filibuster his confirmation. The vote came after Republicans spent years trying to block Cordray’s appointment and attacking the CFPB in court.
The CFPB has already accomplished much to benefit consumers—forcing credit card companies to refund nearly half a billion dollars they juked consumers out of, implementing new rules to make mortgages safer, and creating a center that fields consumer complaints about shady dealings by financial institutions. But without a director confirmed by the Senate, the agency’s powers were limited. Now that Cordray has been confirmed, the CFPB is fully legitimate, Warren says. “There are no more clouds. Period. This locks all the pieces in place,” she told reporters Tuesday.
It was a long struggle. Senate Republicans filibustered Cordray when Obama first nominated him to head the agency in July 2011. In response, Obama used a recess appointment—a presidential appointment that happens while the Senate is on vacation and does not require Senate approval—to install Cordray in January 2012. Republicans then sued to challenge the constitutionality of Cordray’s appointment. Senate Republicans intended to filibuster Cordray again this time around, demanding fundamental changes that would weaken the CFPB before they’d allow a vote. Harry Reid, the Democratic Senate majority leader, threatened to change the rules of the Senate to block the GOP filibuster. But late Tuesday, the Senate devised a truce to avert the Republicans’ filibuster—and Reid’s rule change.
The agency was devised by Warren after the financial crisis, who pointed out at the time that it was “impossible to buy a toaster that has a one-in-five chance of bursting into flames and burning down your house. But it is possible to refinance an existing home with a mortgage that has the same one-in-five chance of putting the family out on the street.” The agency came to life as part of the 2010 Dodd-Frank financial reform act, and Warren has aggressively campaigned for Cordray’s confirmation ever since.
Republicans will continue to push for changes to the agency, such as forcing the agency to be subject to the congressional appropriations process so Congress can revoke its funding and allowing other regulatory agencies to veto CFPB actions. And the Supreme Court will review the constitutionality of Cordray’s previous recess appointment in the fall.
But Warren is not worried. “They can introduce whatever [legislation] they want. The political stalemate is over,” she told reporters, adding that any Supreme Court ruling would have few implications since Cordray now has the Senate’s official approval. As she said in a statement after the Tuesday vote, “The consumer agency is the law of the land and is here to stay.”