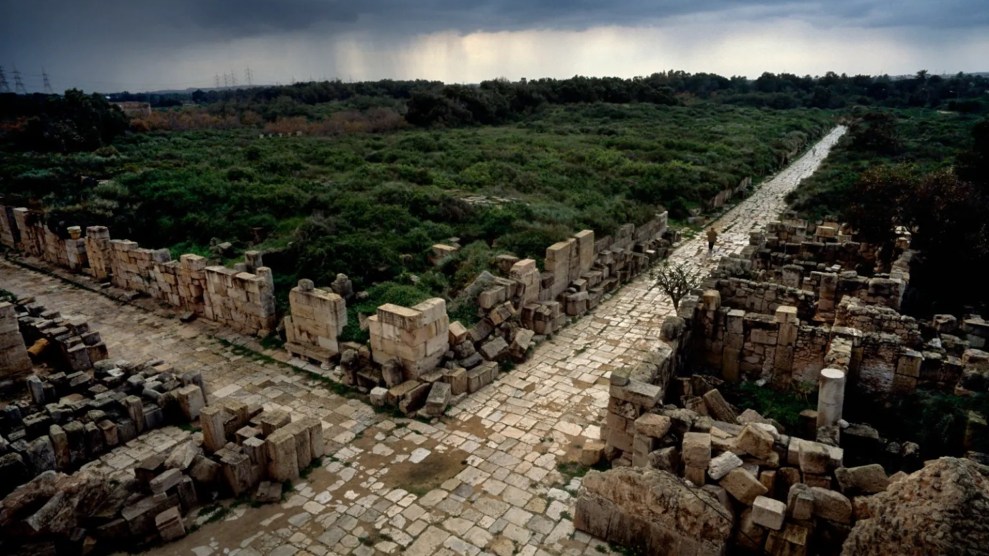
A view of a paved intersection of the ancient Roman roads in Leptis Magna, the largest city of the ancient region of Tripolitania, in modern-day Libya, May 2000. Reza/Getty/Grist
This story was originally published by Grist and is reproduced here as part of the Climate Desk collaboration.
The Roman Empire fell more than 1,500 years ago, but its grip on the popular imagination is still strong, as evidenced by a recent trend on TikTok. Women started filming the men in their lives to document their answers to a simple question: How often do you think about the Roman Empire?
“I guess, technically, like every day,” one boyfriend said, as his girlfriend wheezed out an astonished “What?” He wasn’t the only one, as an avalanche of Twitter posts, Instagram Reels, and news articles made clear. While driving on a highway, some men couldn’t help but think about the extensive network of roads the Romans built, some of which are still in use today. They pondered the system of aqueducts, built with concrete that could harden underwater.
There are a lot of reasons why people are fascinated by the rise and fall of ancient empires, gender dynamics aside. Part of what’s driving that interest is the question: How could something so big and so advanced fail? And, more pressingly: Could something similar happen to us? Between rampaging wildfires, a rise in political violence, and the public’s trust in government at record lows, it doesn’t seem so far-fetched that America could go up in smoke.
Theories of breakdown driven by climate change have proliferated in recent years, encouraged by the likes of Jared Diamond’s 2005 book Collapse: How Societies Choose to Fail or Succeed. The Roman Empire, for example, unraveled during a spasm of volcanic explosions, which led to a period of cooling that precipitated the first pandemic of bubonic plague. The decline of the ancient Maya in Central America has been linked with a major drought. Angkor Wat’s downfall, in modern-day Cambodia, has been pinned on a period of wild swings between drought and monsoon floods. So if minor forms of climate change spelled the collapse of these great societies, how are we supposed to survive the much more radical shifts of today?
Focusing too closely on catastrophe can result in a skewed view of the past—it overlooks societies that navigated an environmental disaster and made it through intact. A review of the literature in 2021 found 77 percent of studies that analyzed the interplay between climate change and societies emphasized catastrophe, while only 10 percent focused on resilience. Historians, anthropologists, and archaeologists have recently tried to fill in that gap. The latest entry is a study that analyzes 150 crises from different time periods and regions, going off a comprehensive dataset that covers more than 5,000 years of human history, back to the Neolithic period. Environmental forces often play a critical role in the fall of societies, the study found, but they can’t do it alone.
Researchers with the Complexity Science Hub, an organization based in Vienna, Austria, that uses mathematical models to understand the dynamics of complex systems, found plenty of examples of societies that made it through famines, cold snaps, and other forms of environmental stress. Several Mesoamerican cities, including the Zapotec settlements of Mitla and Yagul in modern-day Oaxaca, “not only survived but thrived within the same drought conditions” that contributed to the fall of the Maya civilization in the 8th century. And the Maya, before that point, had weathered five earlier droughts and continued to grow.
The new research, published in a peer-reviewed biological sciences journal from The Royal Society last month, suggests that resilience is an ability that societies can gain and lose over time. Researchers found that a stable society can withstand even a dramatic climate shock, whereas a small shock can lead to chaos in a vulnerable one.
The finding is in line with other research, such as a study in Nature in 2021 that analyzed 2,000 years’ worth of Chinese history, untangling the relationship between climate disruptions and the collapse of dynasties. It found that major volcanic eruptions, which often cause cooler summers and weaker monsoons, hurting crops, contributed to the rise of warfare. But it wasn’t the size of the eruption that mattered most: Dynasties survived some of the biggest, climate-disrupting eruptions, including the Tambora eruption of 1815 in present-day Indonesia and the Huaynaputina eruption of 1600 in what’s now Peru.
What matters most, the Complexity Science Hub’s study posits, is inequality and political polarization. Declining living standards tend to lead to dissatisfaction among the general population, while wealthy elites compete for prestigious positions. As pressures rise and society fractures, the government loses legitimacy, making it harder to address challenges collectively. “Inequality is one of history’s greatest villains,” said Daniel Hoyer, a co-author of the study and a historian who studies complex systems. “It really leads to and is at the heart of a lot of other issues.”
On the flipside, however, cooperation can give societies that extra boost they need to withstand environmental threats. “This is why culture matters so much,” Hoyer said. “You need to have social cohesion, you need to have that level of cooperation, to do things that scale—to make reforms, to make adaptations, whether that’s divesting from fossil fuels or changing the way that food systems work.”
It’s reasonable to wonder how neatly the lessons from ancient societies apply to today, when the technology is such that you can fly halfway around the world in a day or outsource the painful task of writing a college essay to ChatGPT. “What can the modern world learn from, for example, the Mayan city states or 17th century Amsterdam?” said Dagomar Degroot, an environmental historian at Georgetown University. The way Degroot sees it, historians can pin down the time-tested strategies as a starting point for policies to help us survive climate change today—a task he’s currently working on with the United Nations Development Programme.
Degroot has identified a number of ways that societies adapted to a changing environment across millennia: Migration allows people to move to more fruitful landscapes; flexible governments learn from past disasters and adopt policies to prevent the same thing from happening again; establishing trade networks makes communities less sensitive to changes in temperature or precipitation. Societies that have greater socioeconomic equality, or that at least provide support for their poorest people, are also more resilient, Degroot said.
By these measures, the United States isn’t exactly on that path to success. According to a standard called the Gini coefficient—where 0 is perfect equality and 1 is complete inequality—the US scores poorly for a rich country, at 0.38 on the scale, beaten out by Norway (0.29) and Switzerland (0.32) but better than Mexico (0.42). Inequality is “out of control,” Hoyer said. “It’s not just that we’re not handling it well. We’re handling it poorly in exactly the same way that so many societies in the past have handled things poorly.”
One of the major voices behind that theme is Peter Turchin, one of the co-authors on Hoyer’s study, a Russian-American scientist who studies complex systems. Once an ecologist analyzing the rise and fall of pine beetle populations, Turchin switched fields in the late 1990s and started to apply a mathematical framework to the rise and fall of human populations instead. Around 2010, he predicted that unrest in America would start getting serious around 2020. Then, right on schedule, the COVID-19 pandemic arrived, a reminder that modern society isn’t immune to the great disasters that shaped the past. “America Is Headed Toward Collapse,” declared the headline of an article in The Atlantic this summer, excerpted from Turchin’s book End Times: Elites, Counter-Elites, and the Path of Political Disintegration.
The barrage of climate catastrophes, gun violence, and terrorist attacks in the headlines are enough to make you consider packing up and trying to live off the land. A recent viral video posed the question: “So is everyone else’s friend group talking about buying some land and having a homestead together where everyone grows separate crops, [where] we can all help each other out and have a supportive community, because our society that we live in feels like it’s crumbling beneath our feet?”
By Turchin’s account, America has been at the brink of collapse twice already, once during the Civil War and again during the Great Depression. It’s not always clear how “collapse” differs from societal change more generally. Some historians define it as a loss of political complexity, while others focus on population decline or whether a society’s culture was maintained. “A lot of people prefer the term ‘decline,’” Degroot said, “in part because historical examples of the collapse of complex societies really refer to a process that took place over sometimes centuries” and would perhaps even go unnoticed by people alive at the time. Living through a period of societal collapse might feel different from what you imagined, just like living through a pandemic did—possibly less like a zombie movie, and more like boring, everyday life once you get accustomed to it.
The Complexity Science Hub’s study suggests that collapse itself could be considered an adaptation in particularly dire situations. “There is this general idea that collapse is scary, and it’s bad, and that’s what we need to avoid,” Hoyer said. “There’s a lot of truth in that, especially because collapse involves violence and destruction and unrest.” But if the way your society is set up is making everyone’s lives miserable, they might be better off with a new system. For example, archaeological evidence shows that after the Roman Empire lost control of the British Isles, people became larger and healthier, according to Degroot. “In no way would collapse automatically be something that would be devastating for those who survived—in fact, often, probably the opposite,” he said.
Of course, there’s no guarantee that a better system will replace the vulnerable, unequal one after a collapse. “You still have to do the work of putting in the reforms, and having the support of those in power, to be able to actually set and reinforce these kinds of revisions,” Hoyer said. “So I would argue, if that’s the case, let’s just do that without the violence to begin with.”