AntonioGuillem/Getty
The Affordable Care Act has led to a massive drop in the amount of money women have to spend on birth control. The law required that plans sold to individuals and insurance offered by employers had to cover a range of contraception options at zero out-of-pocket cost for the subscriber. The Obama administration offered limited exemptions for religious employers, but most workplaces had to include contraception coverage in their insurance offerings. Now, the Kaiser Family Foundation has shown exactly what that policy has meant for women.
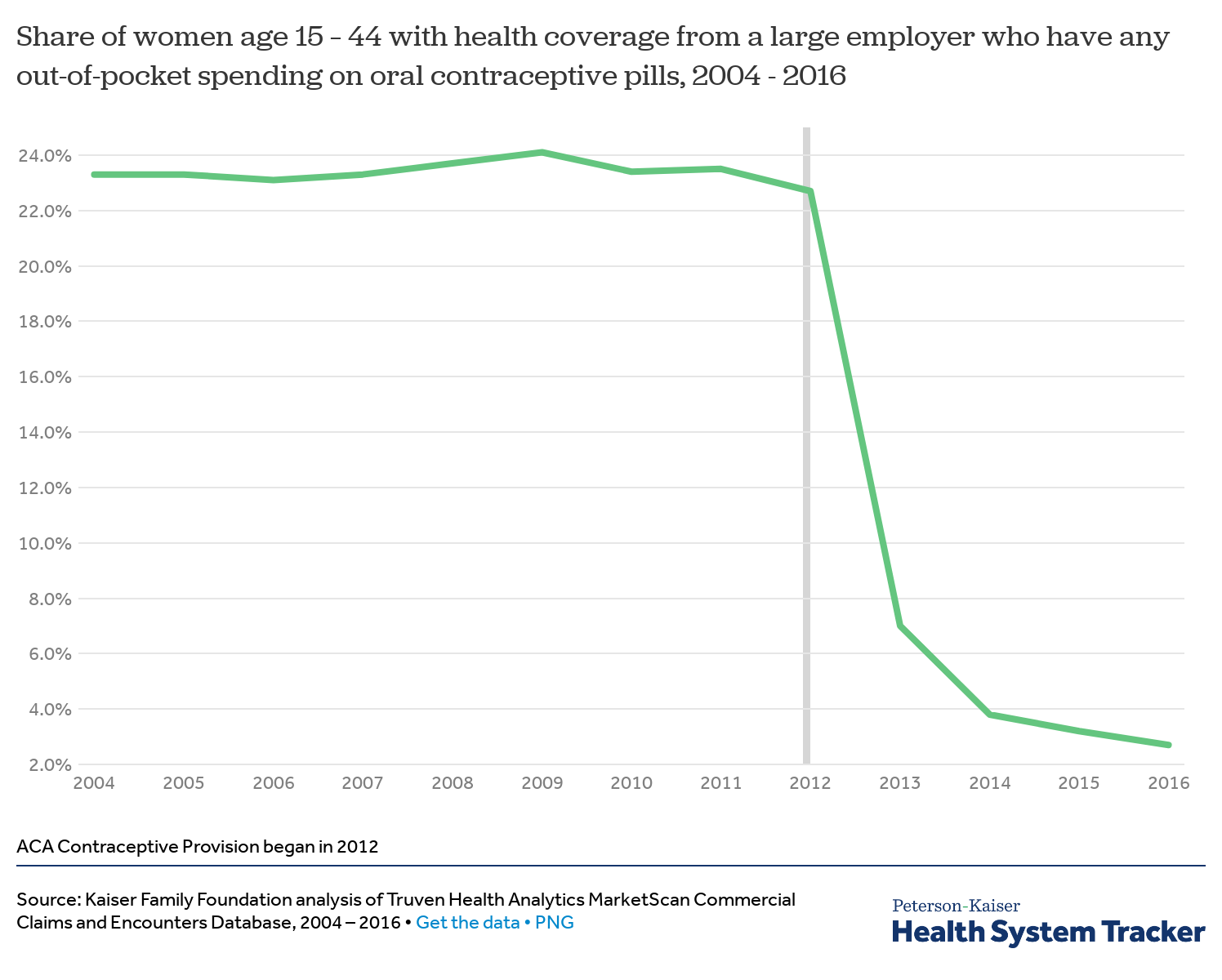
In 2012, the year before the law went into full effect, 22.7 percent of women between the ages of 15 and 44 who got insurance through work paid for at least part of their birth control—right around the same level it had been for a decade. In 2013, that amount instantly dropped to 7 percent, and by 2016, it was all the way down to 2.7 percent. Here’s how it shook out for people who worked for a large employer, via the Kaiser Family Foundation:
A 2015 study published in Health Affairs estimated that women saved $1.4 billion on co-payments for birth control pills during the first year of the ACA’s implementation, an average of $255 per user. And it’s popular, with 68 percent of people supporting the contraception requirement in a poll last year—even a majority of Republicans in favor.
The Kaiser Family Foundation’s analysis only runs through 2016, and there was, of course, a major event in November of that year that shifted federal policy. Last year, the Trump administration vastly broadened the definition of which employers can qualify for an exemption, allowing pretty much any employer to cite a moral or religious belief to duck covering contraception—though legal challenges have kept the implementation of that decision on hold.