Wutzkohphoto/Shutterstock
Approximately 15,600 people died between 2014 and 2017 as a result of their states refusing to expand Medicaid coverage under the Affordable Care Act, according to a new working paper by the National Bureau of Economic Research.
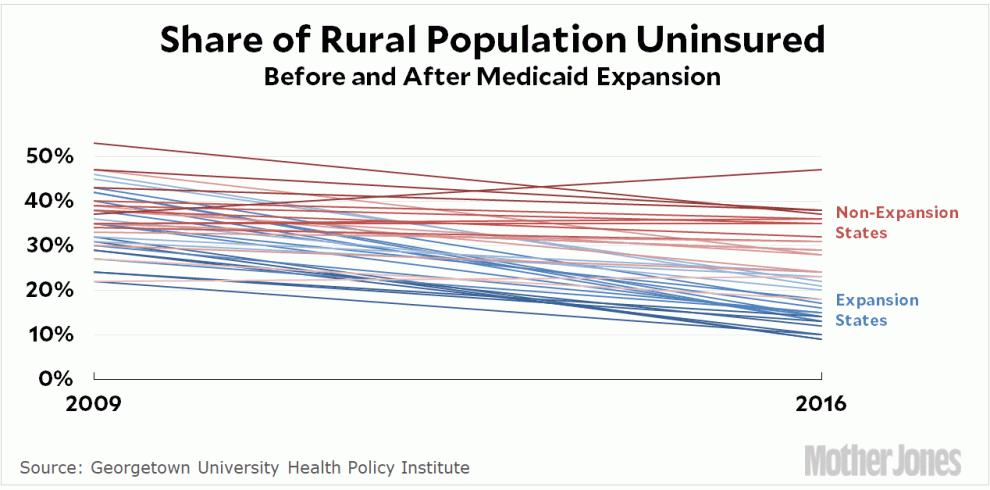
The ACA promised to expand Medicaid coverage to individuals whose income was at or below 138 percent of the federal poverty level, but a 2012 Supreme Court ruling left it up to states to decide whether to expand coverage. Today, 14 states have not adopted Medicaid expansion, and three others have adopted it but not yet implemented it.
The paper studied mortality rates in expansion states and in non-expansion states before and after the increased Medicaid coverage was implemented. It found that, in states that had expanded Medicaid, 4,800 fewer Medicaid-eligible individuals between the ages of 55 and 64 died per year than in non-expansion states.
“Since there are about 3.7 million individuals who meet our sample criteria living in expansion states, our results indicate that approximately 4,800 fewer deaths occurred per year among this population, or roughly 19,200 fewer deaths over the first four years alone,” the researchers wrote. “Or, put differently, as there are approximately 3 million individuals meeting this sample criteria in non-expansion states, failure to expand in these states likely resulted in 15,600 additional deaths over this four year period that could have been avoided if the states had opted to expand coverage.”
Harold Pollack, a health policy expert at the University of Chicago, said that NBER’s finding seemed plausible and that the number of people affected could actually be greater.
“States’ refusal to accept Medicaid is really a hideous policy decision that is largely motivated by partisan spite,” he said. “There’s some states that will abandon some of their neediest citizens, and some of the neediest citizens will have horrible outcomes.”
Several Republican governors have refused to expand Medicaid in their states, even though the federal government finances most of the costs of expansion, likely because the legislation is associated with Barack Obama’s presidency. Still, Medicaid expansion polls well even in red states, and has been favored by voters in states with Republican governors, such as Utah.
The new study provides a formidable justification for Medicaid expansion, as it has been shown to save lives. Medicaid expansion was particularly effective in reducing preventable deaths related to conditions such as cardiovascular disease, the study found.
Pollack pointed out that Medicaid still has room to improve in several areas, including its payments to medical providers, coverage for mental illness, and treatment of the opioid epidemic. “If we were using Medicaid in the most powerful way as a pubic health intervention, the states that have expanded Medicaid would have found more benefits that they seem to be finding,” he said. “I would like to see us do a better job of operating Medicaid in the states that are really trying to do it right.”